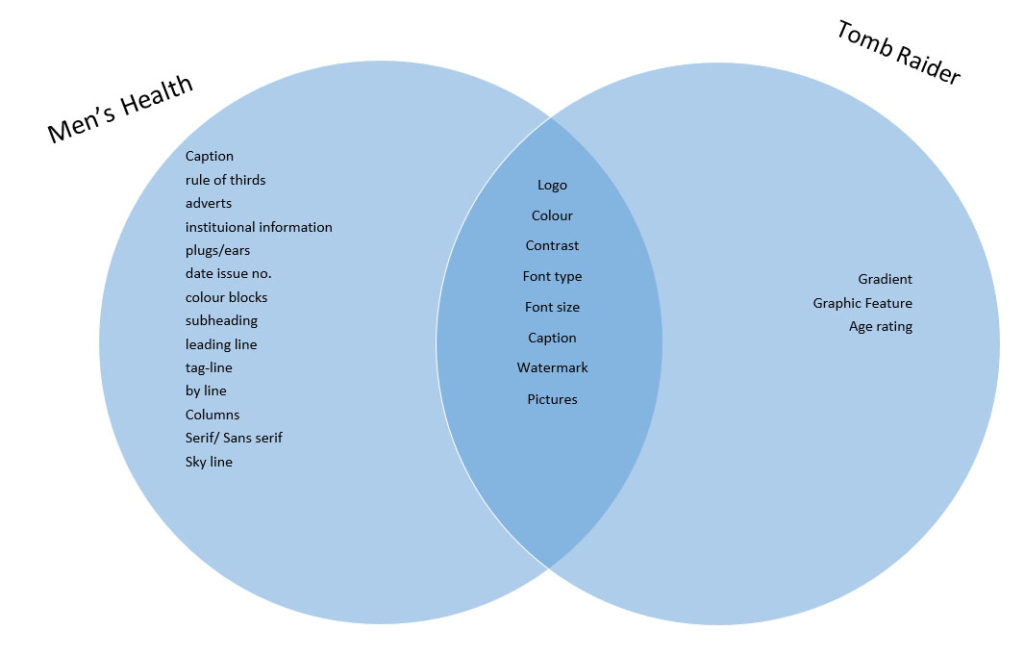
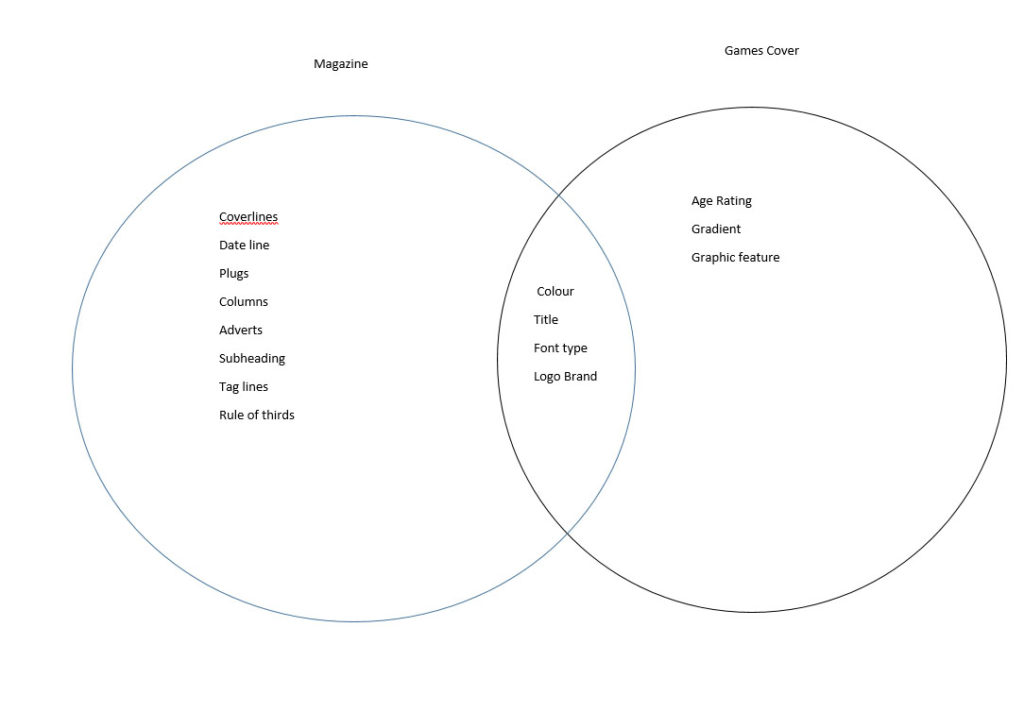
Positive stereotype – A positive stereotype represents a “positive” evaluation of a social group.
Negative stereotype – A negative belief held against a social group.
Counter-types – a positive stereotype and emphasizes the positive features about a person. Used to break and go against the current stereotype.
Misrepresentation – the action of giving a false or misleading account of the nature of something.
Selective representation – when some groups of people are represented more in government than others.
Dominant ideology – attitudes, beliefs, values, and morals shared by the majority of the people in a given society
Constructed reality –the theory that the way we present ourselves to other people is shaped partly by our interactions with others, as well as by our life experiences.
Hegemony – leadership or dominance, especially by one state or social group over others.
Audience positioning – the techniques used by the creator of a text to try to get the audience to understand the ideology of the text
Fluidity of identity – Identity is not fixed to a person, it can be changed or altered.
Constructed identity –
Negotiated identity – the processes through which people reach agreements regarding “who is who” in their relationships
Collective identity – the shared sense of belonging to a group