Steve Neale states that genres all contain instances of repetition and difference, the difference is essential to the economy of the genre. Neale states that the film and its genre is defined by two things: How much is conforms to its genre’s individual conventions and stereotypes.
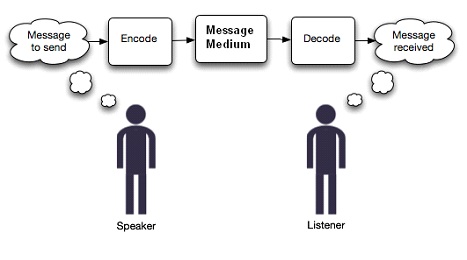
Genre Theory is a collective term used to describe theoretical approaches that are concerned with how similar situations generate typified responses called genres, which serve as a platform for both creating an understanding based on shared expectations and also shaping the social context.
The word genre comes from the French (and originally Latin) word for ‘kind’ or ‘class’.
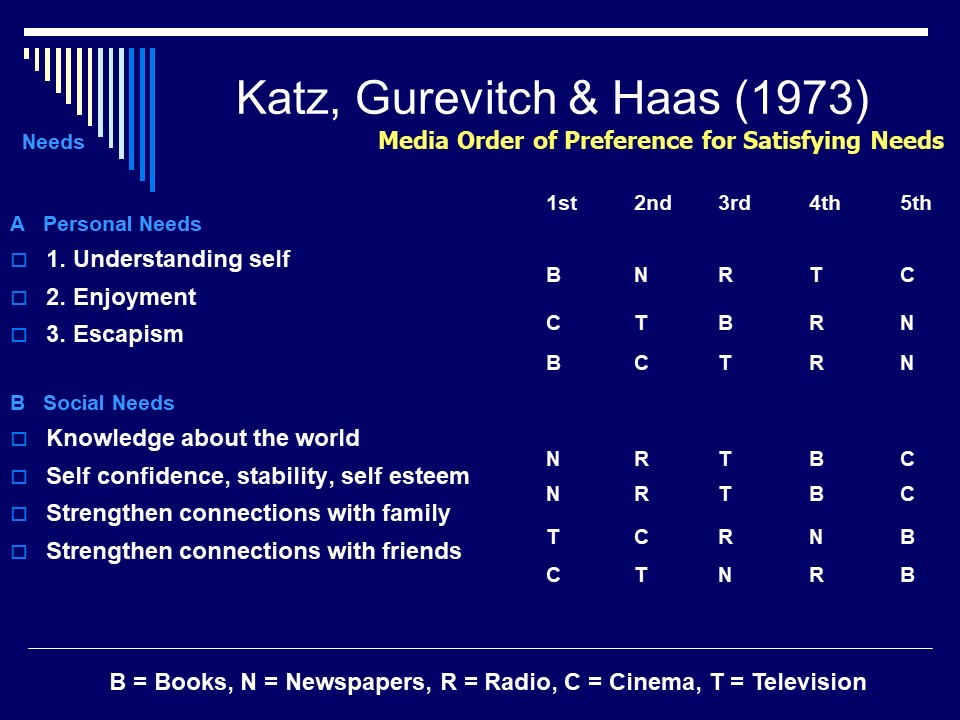
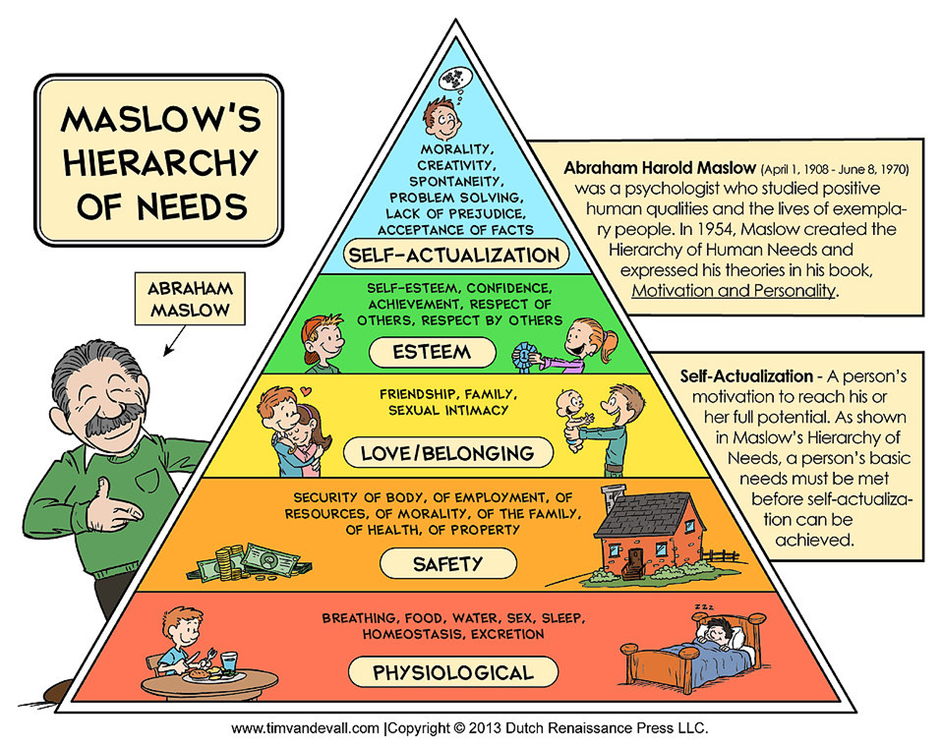
Genre is important for both consumers and media producers. Consumers can make choices about media texts they wish to consume and media producers can create a media text for a specific audience. Audiences will also expect certain audio codes such as tense, dramatic music.