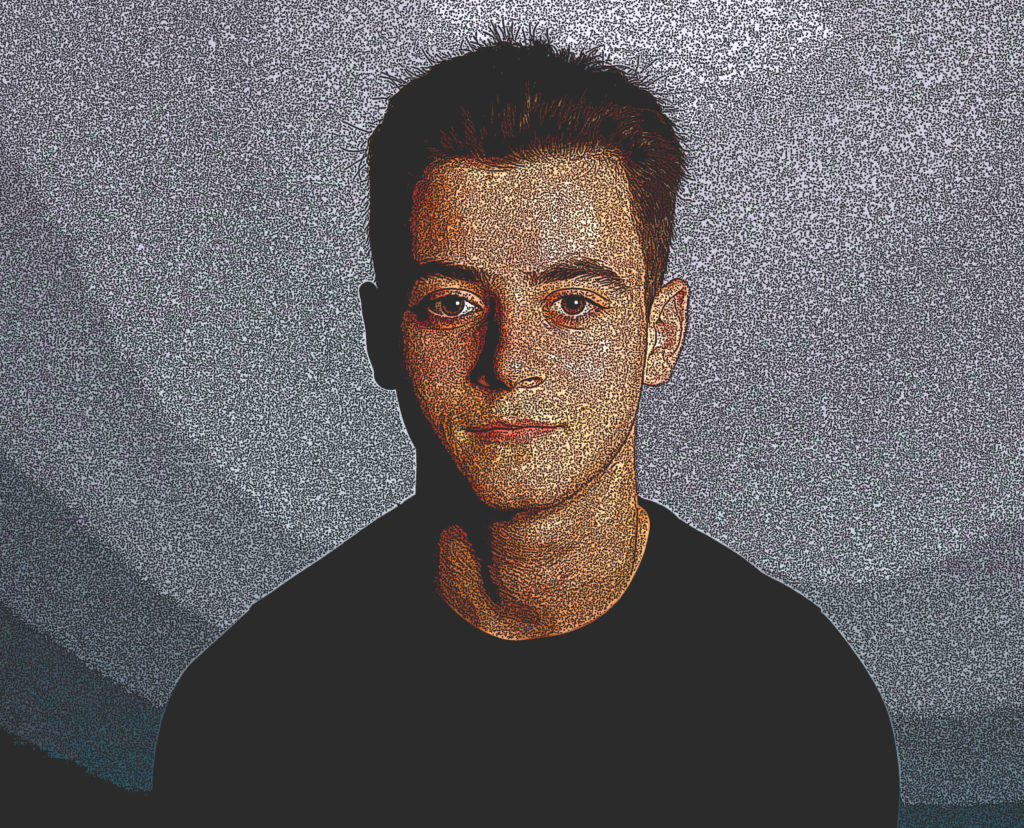

Character Editing
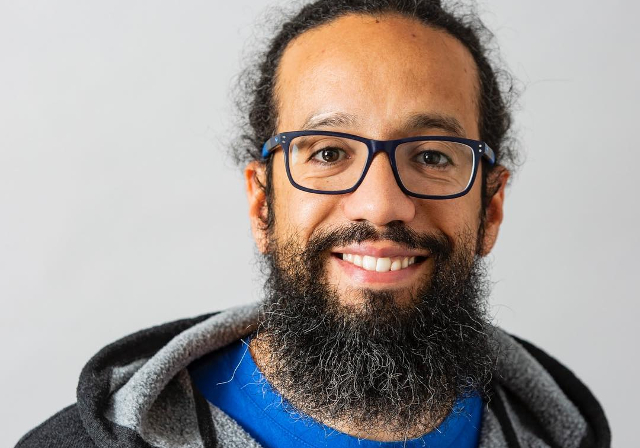




My character is:

It is a games magazines, and have got inspiration from Games TM and PC Gamer. My intention is to create a magazine cover that covers reviews, tips and a front cover that bases about a gun slinging open-world game. It also contains plugs, puffs and a skyline with a large image in the centre.
My target market is primarily for teen men but this is a generalization as anyone can be into video games












As more people can access the internet and therefore get their information online which is quicker so less people will go out to buy a magazine. By the time the magazine is created and published, the news could be old or irrelevant by the time someone buys a magazine. Also websites are usually free and so people may not want to pay for information. Magazines also take up environmental resources by cutting down trees for paper.
Barthes – French literary theorist, philosopher, critic, and semiotician. Barthes’ ideas explored a diverse range of fields and he influenced the development of many schools of theory, including structuralism, semiotics, social theory, design theory, anthropology, and post-structuralism.
Pierce – American philosopher, logician, mathematician, and scientist who is sometimes known as “the father of pragmatism”. He was educated as a chemist and employed as a scientist for thirty years
Saussure – Swiss linguist and semiotician. His ideas laid a foundation for many significant developments in both linguistics and semiology in the 20th century. He is widely considered one of the founders of 20th-century linguistics and one of two major founders of semiotics/semiology
Semiotics – the study of signs and symbols and their use or interpretation.
Sign – a gesture or action used to convey information or an instruction.
Signifier – a sign’s physical form (such as a sound, printed word, or image) as distinct from its meaning. (Saussure)
Signified – the meaning or idea expressed by a sign, as distinct from the physical form in which it is expressed. (Saussure)
Icon – a person or thing regarded as a representative symbol or as worthy of veneration.
Index – (in a book or set of books) an alphabetical list of names, subjects, etc. with reference to the pages on which they are mentioned.
Symbol – a thing that represents or stands for something else, especially a material object representing something abstract.
Code – a system of words, letters, figures, or symbols used to represent others, especially for the purposes of secrecy.
Dominant Signifier – The main sign
Anchorage – Meaning of a sign
Ideology – a system of ideas and ideals, especially one which forms the basis of economic or political theory and policy.
Paradigm – a group/collection of similar things
Syntagm – a linguistic unit consisting of a set of linguistic forms (phonemes, words, or phrases) that are in a sequential relationship to one another.
Signifcation – the representation or conveying of meaning.
Denotation – the literal or primary meaning of a word, in contrast to the feelings or ideas that the word suggests. (Barthes)
Connotation – an idea or feeling which a word invokes for a person in addition to its literal or primary meaning. (Barthes)
Myth – a belief that lots of people believe in however it isn’t true.
Dominant Ideology – the attitudes, beliefs, values, and morals shared by the majority of the people in a given society
A Radical Text – Text that challenges the dominant ideology
A Reactionary Text – Text that supports the dominant ideology