> Semiotics
Roland Barthes – Connotation, Denotation and Myth
De Saussure – Signifier and Signified
C S Pierce – Iconic, indexical and symbolic
Syntagm – Combination of images and words
Paradigm – how we can create differentiation in meaning via small changes.
> Narrative
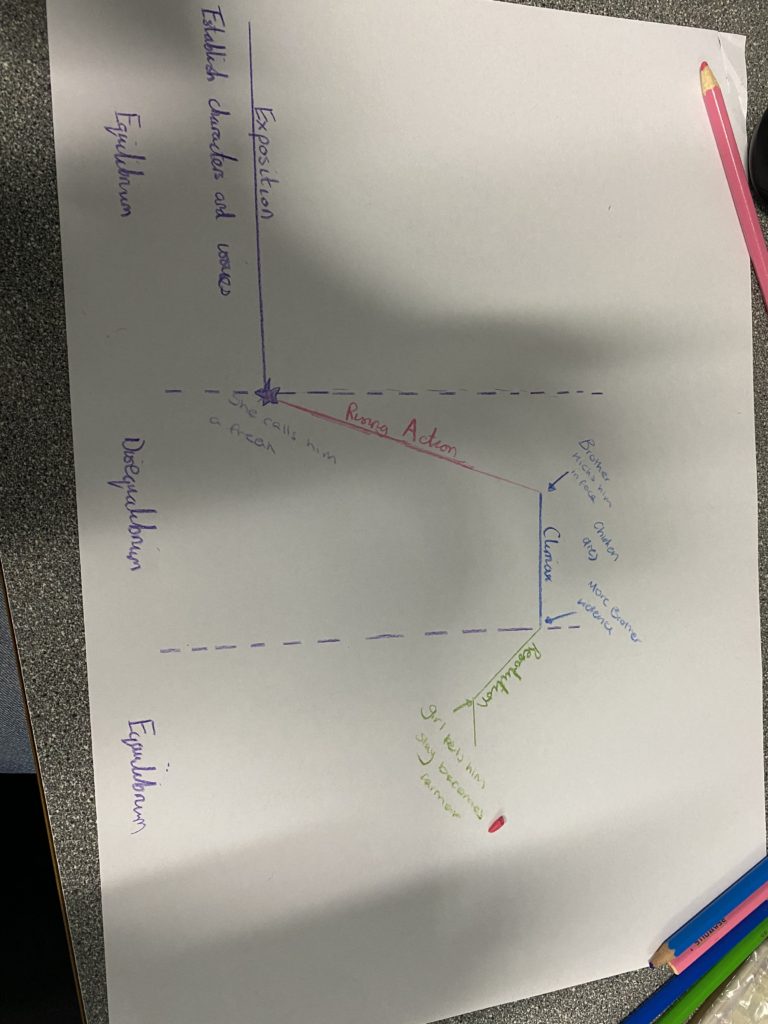
Todorov – Equilibrium, disequilibrium, back to equilibrium
Propp – Character types such as hero, dispatcher, princess
Levi-Strauss – Binary oppositions
Freytag – Inciting incident, rising action, climax, falling action – 3 acts
Chatman – Satellites and Kernels
> Genre
Steve Neale – Repetition of similarity and differences. Verisimilitude and diegesis.
> Postcolonialism
Edward Said – Orientalism – they cant represent themselves, they are viewed as stereotypes by the West.
Jaques Lacan – The ‘other’, mirror stage at 3.
Franz Fanon – Wretch of the Earth – ‘mechanics of colonialism and its effects of those it ensnared‘ – racial stereotyping, derogatory abuse – as acceptable social interaction due to society ideas
Gilroy – Double Consciousness – multiple identity such as black and French. Hybridity – being a part of multiple identities. Syncretism – hybrid of multiple cultures.
Althusser – ISA
Gramsci – Cultural hegemony and hegemonic struggle
Ghost Town – British yet represents multiple music genres such as ska, pop – multicultural. United protest against Thatcher.
> Representation
> Feminist Critical thinking
Laura Mulvey male gaze and female gaze. Idea of scopophilia (pleasure of looking) and fetishism (cuts of different parts) – 1st Wave
Judith Butler – gender as a performance – multiple identities that are performed to different people, in different social settings, under different social conditions
bel Hook’s – multicultural – multiple identities including racism, gender, sexuality such as female and gay
Van zoonen – also that woman are not fixed as one thing but are intersected with other thing such as race. They are permanently being reconstructed.
> Liberal Free Press
> Transformation of Public Sphere
Habermas – Transformation of Public Sphere
> PSB
Curran ~ Seaton – Diverse landscapes – PSB such as BBC
Livingston & Lunt ~ Regulation – cultural health vs consumer
Hesmondhalgh – Risky Business –
> Ideology
> Audience theories
Gerbner ~ Cultivation Theory – ‘television cultivates from infancy the very predispositions and preferences that used to be acquired from other primary sources‘ – media (mainly tv) shapes the way people think
Hall ~ Reception/Preferred Reading Theory – different views such as hegemonic/negotiated/oppositional depending on different people – audiences are active in making opinions
Lasswell ~ Hypodermic – passive
Lazarfeld ~ 2 Step Flow – active
Shirky ~ End of Audience – the more ideas there are in circulation, the more ideas there are for any individual to disagree with.
Zuboff- Servaince Capitalism as the meida moinotrs us
Jenkins – Media is created through audience feedback – a shift in the public’s role in the political process
> reception theory / theory of preferred reading
> Cultivation theory
> Culture, politics, history
> (Fandom / Moral Panic)