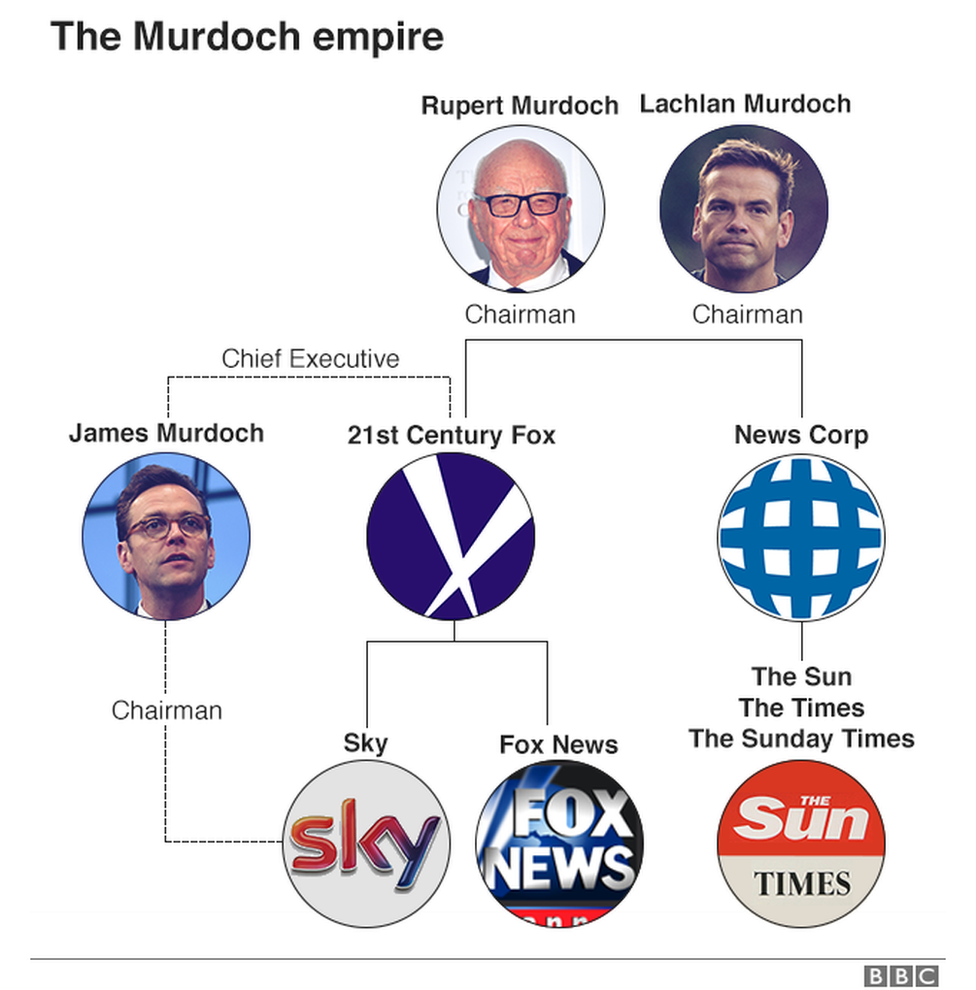
Althusser:
“All ideology hails or interpellates concrete individuals as concrete subjects, through the functioning of the category of the subject.” – 1971
Althusser said that society is structured to keep you in your place & coined the phrase ‘socially constructed’. The ruling ideology (the ideas of the ruling class) constructs us. He says we cant escape, we are interpellated in this system which relates to Orientalism since the ‘other’ do not have the power to represent themselves. Ideological state apparatus (ISA) describes all the things which have an impact on us & makes us who we are, the way society encodes you is called interpellation, it shapes us, forced to look & think
In the sense of The daily mail, they has had a lot of criticizing accusations made against them such as racism, sexism and blasphemous accusations as well as clearly supporting the conservative political party who are right wing, meaning they hold traditional values. In terms of the latter, to endorse the conservative party they published an article in 2013 which criticized Ralph Milliband, father of Ed Milliband – the then labor leader, titled “The Man Who Hated Britain”. In the article, the writer Geoffrey Levy attacked Ralph as he is a Jewish refugee from the Holocaust saying that “his son was determined to bring back socialism in homage to his father.” Levy also wrote “As for the country that gave him and his family protection, the 17-year-old wrote in his diary: ‘The Englishman is a rabid nationalist.'” Ed Miliband said that the article was “ludicrously untrue”.
This antisemitism view shows how the news tries to shape our opinion and this Daily Mail article tried to boost the conservative party so more people would vote for them as well as paint the Jewish in a negative light, relating to the fact that Althssur said that the ruling ideology constructs the ‘other’ who do not have the power to represent themselves. (Orientalism)