Media concentration
Concentration in the mass media industry is a pattern of ownership where fewer and fewer people own more and more of the assets of that industry.
Conglomerates
Media conglomerate describes companies that own large numbers of companies in various mass media such as television, radio, publishing, movies, and the Internet.
Globalisation
media globalization is the worldwide integration of media through the cross-cultural exchange of ideas, while technological globalization refers to the cross-cultural development and exchange of technology.
Vertical Integration
– Vertical integration is a strategy whereby a company owns or controls its suppliers, distributors or retail locations to control its value or supply chain. Vertical integration benefits companies by allowing them to control process, reduce costs and improve efficiencies.
Horizontal Integration –
Horizontal integration is the process of a company increasing production of goods or services at the same part of the supply chain. A company may do this via internal expansion, acquisition or merger. The process can lead to monopoly if a company captures the vast majority of the market for that product or service.
Gatekeepers-
Gatekeeping occurs at all levels of the media structure—from a reporter deciding which sources are chosen to include in a story to editors deciding which stories are printed or covered and includes media outlet owners and even advertisers. – Somebody who exerts power.
Regulation / Deregulation-
Deregulation is when the government reduces or eliminates restrictions on industries, often with the goal of making it easier to do business. It removes a regulation that interferes with firms’ ability to compete, especially overseas. By banks etc prevents monopolies. – it is hard to regulate new media companies such a google and amazon.
Free market vs Monopolies & Mergers-
A free market is one where voluntary exchange and the laws of supply and demand provide the sole basis for the economic system, without government intervention. A key feature of free markets is the absence of coerced (forced) transactions or conditions on transactions. Monopolies-owing everything.
Neo-liberalism and the Alt-Right –
Neoliberalism is antithetical to the protection of group – rather than individual – interests, for example, that might be achieved through lobbying of groups, or state interventions that protect national interests via tariffs or subsidies. Neoliberalism has moved away from a centrally governed economy. ideological grouping associated with extreme conservative or reactionary viewpoints, characterized by a rejection of mainstream politics and by the use of online media to disseminate deliberately controversial content.
Surveillance / Privacy / Security / GDPR-
lose observation, especially of a suspected spy or criminal.
David Hesmondhalgh
David Hesmondhalgh is among a range of academics who critically analyse the relationship between media work and the media industry. In his seminal book, The Culture Industries (Sage, 2019) he suggest that:
“the distinctive organisational form of the cultural industries has considerable implications for the conditions under which symbolic creativity is carried out“
A critical reflection that highlights the ‘myth making’ process surrounding the potential digital future for young creatives, setting up a counter-weight against the desire of so many young people who are perhaps too easily seduced to pursue a career in the creative industries- compliance.
Looking for work in creative industries policy. International Journal of Cultural Policy p.428
An its utopian presentation, creative work is now imagined only as a self-actualising pleasure, rather than a potentially arduous or problematic obligation undertaken through material necessity (2009, p. 417)
Hesmondhalgh’s theory: This suggests that cultural industry companies. Minimise risk + Maximise Audiences = Maximise Profit.
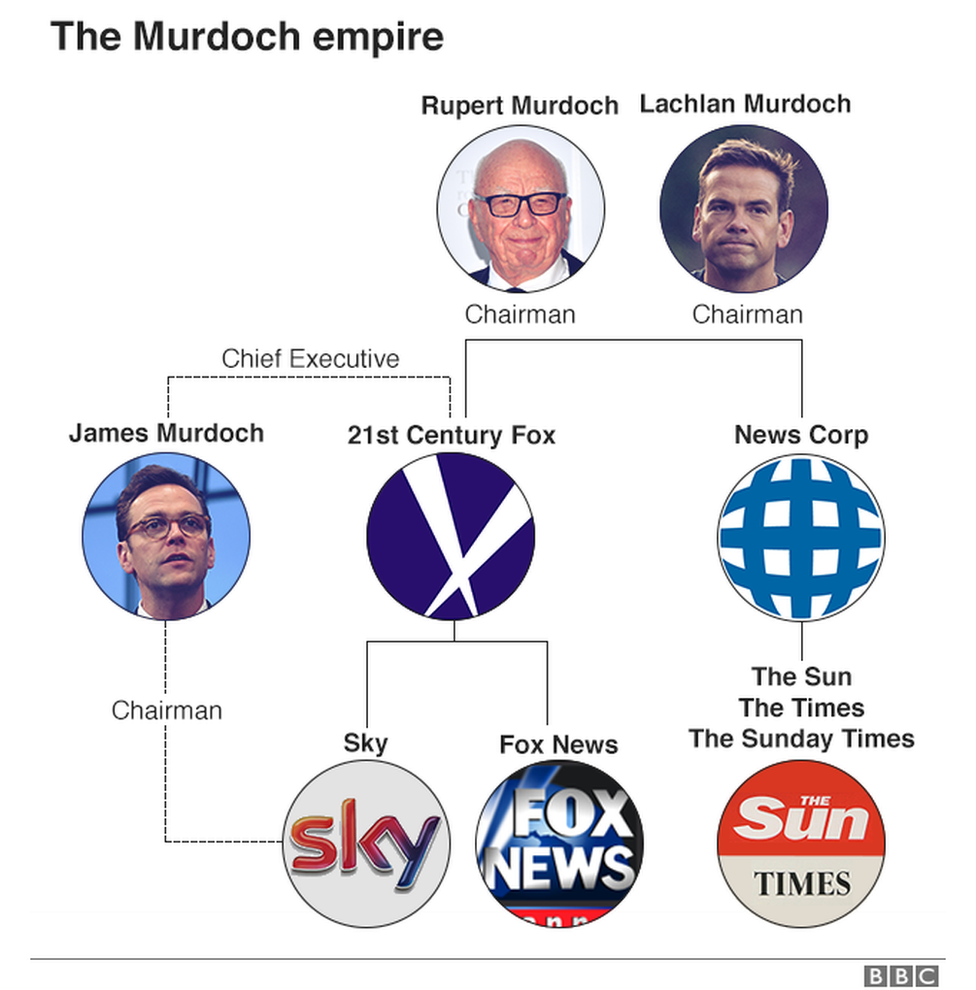
Rupert Murdoch- Media empire
Murdoch’s media empire includes Fox News, Fox Sports, the Fox Network, The Wall Street Journal, and HarperCollins. In March 2019, Murdoch sold the majority of 21st Century Fox’s entertainment assets to the Walt Disney Company for $71.3 billion. Founded: Sky News, BSkyB, News Corp, Fox News
noam Chomsky
- press freedom
- manufactoring consent- media acts as a check on political power, informs the public and manufacture our consent.
- media and politics are intertwined
- media stages democracy
- 5 filters:
- ownership – for profit part of larger conglomerates , out for profit media journalism accuracy takes second place.
- advertisers close the gap, to create good publicity for what they support- advertisers pay for audiences.
- when the story is unconfident to the media- it is diverted.
- we think we are free however, we are being controlled and we don’t see society how it really is and are manipulated by what is told to them in the media.
Media working practices
Rupert Murdoch is so succesful that his decision to support labour, impacted the new labour party election in 1997. Becuase of his ownership of The sun, the times and news of the world. These newspapers promoted the labour goverment and leader Tony Blair. The police accepted briebs from Murdochs company to gain data from them, however nothing was ever done about it. This is an example of Murdoch’s power and the influence his media companies can have on society.
hesmondhalgh’s theory talks about theories of the self and identity in relation to aspirational ambitions and the realities of the creative economy. He critically analyses the relationship between media work and the media industry. How it is romanticised vs the reality of the industry. academics
CURRAN AND SEATON
- Liberal theory is the freedom to to publish in the free market
- “ensure that the press reflects a wide range of options and interests in society.”- (The liberal theory of press freedom)
- “the press is the peoples watchdog, scrutinising the actions of the government and holding the countries rulers to account.” – the press is the way of providing information to the public about what is happening in the world which gives flack to the government. – curran
- the advances of technology means that nearly anyone is free to publish whatever they like for a smaller amount of money.
- In the 80’s new technologies came out and therefore should have increased the number of newspapers being produced however it didn’t, there are still the same amount of papers. This proves his theory that there is not enough diversification in the press. This can effect the American election as it may impact who people vote for. The press can do this by showing a candidate in a certain light.
- The free market, it is also argued to makes the press a representative institution.
- the market of press is independent because it owes allegiance only to the public
- the press complains commission (PCC) was established in 1991
- British broadcasting was started as a public service, and this proved as creative commercially as it was innovative culturally