gaming magazine made for 12+
action adventure game
released in November 2002
gaming magazine made for 12+
action adventure game
released in November 2002
Overview

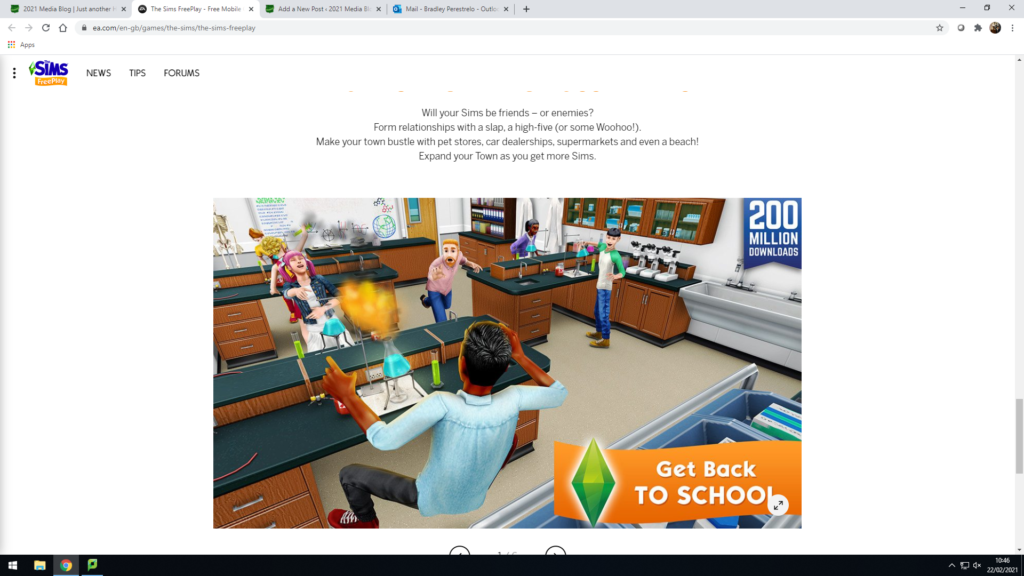
– The Sims FreePlay is a strategic life simulation game developed by EA Mobile and later with Firemonkeys Studios.
– In The Sims FreePlay, players “build” and design houses and customize and create (a maximum of 34) virtual people called Sims.
– Players can control their Sims to satisfy their wishes, and let them complete different kinds of actions to gain Simoleons, Lifestyle Points, and Social Points (all three currencies in the game).
– The game features four types of currency: Simoleons, Lifestyle Points, Social Points, and Simcash, the latter being obtainable by spending real currency
– The tasks within the Sims will be completed in real time
– The Sims FreePlay is a spin-off from the hugely successful Sims franchise first published by Electronic Arts (EA) in 2000.
– Sims Freeplay is marketed to predominantly youth audience.
Theorists:
– Tells you what a sim needs to live = Maslow’s Hierachy of Needs
– The Sims franchise is one of the best examples of Henry Jenkins’ concept of participatory culture.
– Open ended nature – Todorov only applied to micro-narratives rather than to larger meta narratives (i.e. completing each task)
– Propps Character Types:
Hero: The Sim avatar
Villain: Sim’s needs and desires
Princess: Experience for the player
Dispatcher: Task system that tells you what to do next
Helper: Jobs and money
Doner: Game’s items store
– Media Theorists to apply:
Van Zoonen – gender stereotypes
bell hooks – power structures in society
Gauntlett – fluidity of identity
Gilroy – double consciousness
Hall- approaches to representation /encoding and decoding
Gramsci – marxism and hegemony
Strinati – post modernism (5 ways to identify : 1 and 4 apply to Sims)
Baudrillard – hyperreality theory blurring lines between fiction and reality
–
links to post modernism – everything superficial and hyperrealistic
parody – copying real life – remaking friends, celebrities etc
developed by EA Mobile and later with Firemonkeys Studios
free version of The Sims for mobile devices
released for iOS on December 15, 2011
released for Android on February 15, 2012
released for BlackBerry 10 on July 31, 2013
released for Windows Phone 8 on September 12, 2013
released for Fire OS in October 2012
game features four types of currency: Simoleons, Lifestyle Points, Social Points, and Simcash, the latter being obtainable by spending real currency
Sims Freeplay received “Generally favorable reviews” from critics, holding an aggregated Metacritic score of 80/100
The video game was banned due to the possibility of establishing a homosexual relationship in: China, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Oman, Kuwait, Qatar and Egypt
create people of alls sorts of gender style – creative thing
the representative for ea told fans on an online forum that sims mobile game the sims freeplay will no longer be available in 7 countries – spokesperson said “in light of regional standard” the game will no longer be updated. -it was banned due to games explicit LGBT CONTENT.
immerses people to be able to escape their real life and give people control over peoples hyperreality life
Open system -any body can play it – however due to the ban it is now considered as a closed system, as countries like china and saudi arab cannot play the game
Active involvement- play game. and transferring money
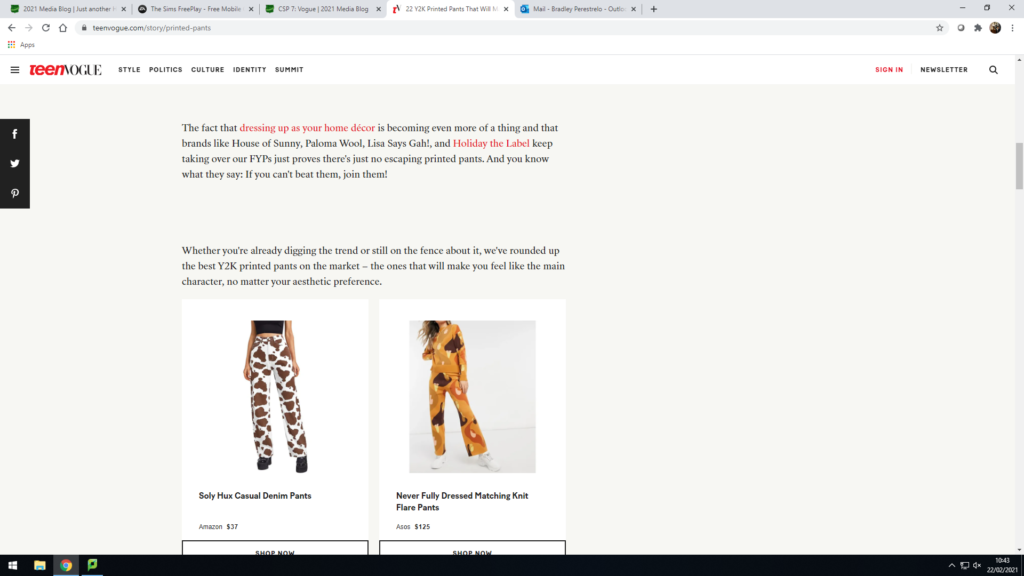
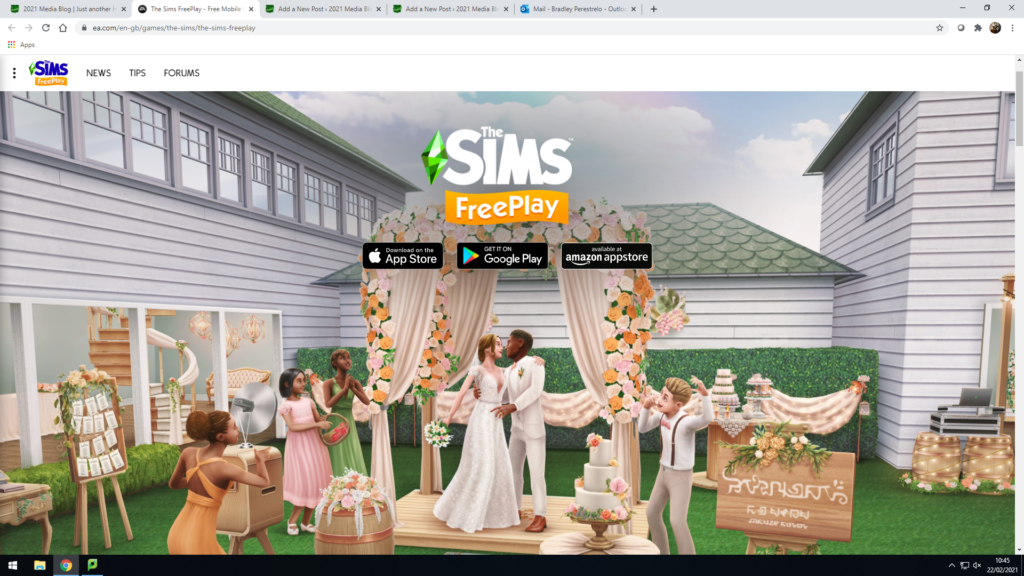










Ok this is it!!! Our last topic for this A level course – hope you have had some fun, learned some things and generally developed as a human being!!
This last topic actually includes 5 SEPARATE CSP’s and is organised under the umbrella term: ON-LINE, SOCIAL AND PARTICIPATORY MEDIA.
For this course, the study of Online, Social and Participatory media and Video Games is linked. You will study some Online Social and Participatory media products (Teen Vogue and The Voice) and you will study some video games (Metroid and Tomb Raider Anniversary). You will also study SIMs Freeplay. For this product you will study both the game and its online, social and participatory media products. This will help you develop your understanding of the digitally convergent nature of media products. The list below makes it clear what you need to study.
These CSP’s need to be studied in terms of ALL 4 CONCEPTUAL AREAS:
For many the rise of a new media society is closely linked to the theoretical position of POSTMODERNISM, so a basic grasp of some of the ideas behind this key concept would also help
As this is quite a lot to refer to I will use this post for general ideas and approaches, so PLEASE REFER TO THE STUDENT CSP BOOKLET for SPECIFIC GUIDANCE.
poster and front cover


Argument = how new technologies has shaped the way audiences consume media.
Paragraph 1:
– Introduce the CSPs briefly
– Historical context
– Technological Advancements
– WOTW was very serious broadcast whereas LH is more casual, shift in society
– WOTW has very iconic sounds, whereas LH has more symbolic for entertainment purposes
– LH tagret audience of teens/young people
– WOTW target of more adults
WOTW overdramtises such as how they say 40 minutes in: I am obsessed with the thought I am the last living man on Earth. people believed this as they couldnt check on google
Paragraph 2:
– PSB
– Mentioning how BBC has a subscription service and its been increased this year
– How the target audience of LH and WOTW has changed
– Social changes
– Clay Shirky end of audience theory
– Henry Jenkins and participatory culture/fandoms
– Hesmondhalgh and how the media is a risky business
– Laswells communciation model and how theres been a shift in audience participation and people now are more media literate. LH includes audience participation such as texting in whereas WOTW doesn’t
Paragraph 3:
– Start to wrap up
– Talk about Stanley Cohen and Folk Devils and Moral Panics and how WOTW links to this
– Cultivation theory and how Gerbners theory links to the spreading of fake news in WOTW
– WOTW spreads propaganda and was provately funded through ads whereas BBC LH is funded by peoples subscriptions
– New media makes users sign into BBC and they can see analytics on what users click on and how long theyre on pages for
– Stuart Hall and theory of preferred reading based on how the BBC LH does shows based on social situations and people can text in with questions
Paragraph 4:
– Conclusion
– both CSPs differ
– Technological advancements
war of the worlds – laswell hypodermic 1920 – 30 – more passive audience – all a one way system
life hacks – theorist more currently – clay shirky – the end of audience – more collaborative and interactive as audience can speak in
theorist
1920/30 – lasswell hypodermic shannon
1940 – shannon + weaver – lazarfield 2 step flow
1960 – uses and grats
1970 – gerbner – skinner v chomksy
1980 – stuart hall – preferred reading
2000 – clay shirky
2019 – zuboff surrillane capitalism
War of the Worlds radio drama had left listeners into suspended disbelief and became famous because it tricked people into believing aliens were invading Earth due to the “breaking news” style of the broadcast. Plot contains Martians invading new Jersey. People in the 1900’s had less knowledge and were more naïve when it came to media/news –Passive audience/targets a niche audience. The science fiction drama was broadcasted from CBS, which is the Columbia Broadcasting System. It is a radio podcast of a science fiction novel that was written by H.G Wells. All in all CBS radio’s ultimate goal was to create publicity. On it’s opening evening, it was estimated that around 30 million people were tuning into the broadcast and around 80% of Americans owned a radio then. The New York Times headlined a quote that stated ‘Radio listeners in panic, taking war drama as fact’. The idea of a ‘risky business’ and being hard to meet everyone’s needs. Not being able to predict if an audience will enjoy what is being created. – Hesmondhalgh. Clay Shirky- Audience behavior has changed due to the internet and the ability for audiences to create their own content at home thanks to the lower cost of technology. This new audience doesn’t just consume media, but also produces it – creating the term ‘presumer’. Influence of new technology – New media reaches a different and wider network of people/viewers.