Revisit Practical Work
As part of our revisit, revise, re-cap, I want to spend the rest of this half term going back over our practical work. Roughly, this means:
- a week on the music print briefs (producing drafts for all four products) see image below
- a week on the music video – a time to experiment, play and produce
- 2 weeks (after half term) to complete your chosen A2 NEA
- So you also have the 1/2 break to complete and organise your A2 NEA.

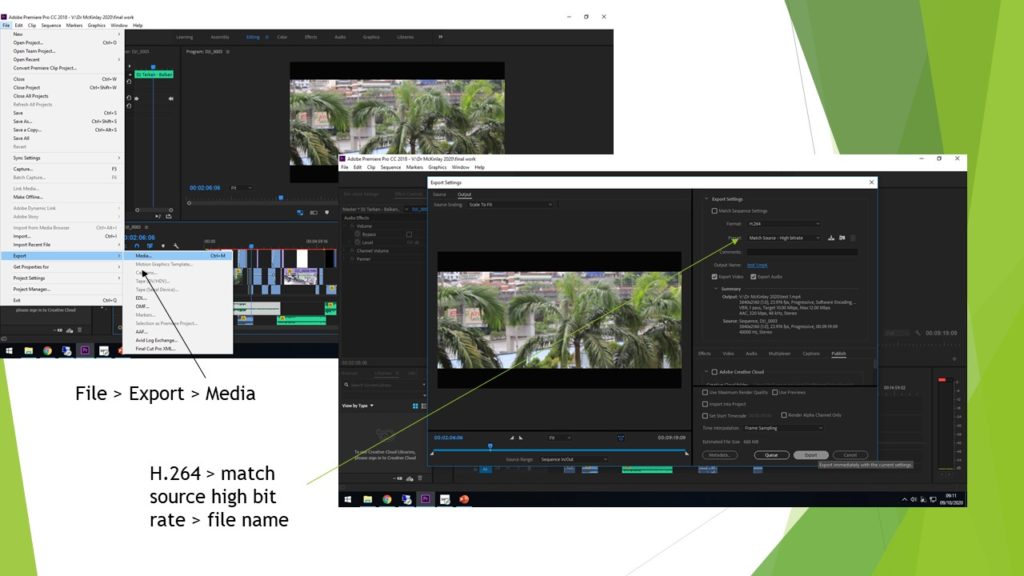

Now that you have completed your A2 NEA (ie your AS magazine and your 3 related adverts please refer to previous communications), we can now start producing some A2 creative work.
As ever, please follow my instructions carefully. As you should have realised by now, the best way to produce your best work IS NOT TO LEAVE IT ALL TO THE LAST MINUTE! 😌
Q: WHAT ARE YOU GOING TO DO?
A: YOU ARE GOING TO . . . IMA G INE . . .

REFLECTION
As we have been recently looking at MUSIC VIDEOS – that have both had a central theme of ISOLATION – I want you to . . . Imagine a music video in which the main character(s) is/are isolated listening to music on headphones.
Just to repeat – you must feature HEADPHONES in your imaginary music video.
Just to repeat – the theme is ISOLATION. So please try to draw upon the ideas that were raised on the POST COLONIAL post (link) think for example, about the meaning of DIASPORA and/or DOUBLE CONSCIOUSNESS and/or . . . In many ways, the video is probably going to be about IDENTITY so feel free to visit this post on REPRESENTATION, IDENTITY & SELF which will also give you some theoretical ideas to trigger off your i m a g i n a t i o n . . .
THEN WHAT?
PRE-PRODUCTION 1
BRAINSTORM
1 Produce and upload a mood board that visually reflects this idea.
- Make sure you mood board has at least 20 images.
- Make sure you images have people and places in them.
- Look for colours, shapes, angles and shot sizes
- Add in anything that helps to communicate your ideas adn reflects and represents your ideas visually.
DEADLINE
Please embed your mood board into a new blog post by FRIDAY 15th MAY (so DO NOT make a link – embed as JPEG!! This is a media course 😣)
Q: What is a mood board?
A: It’s fairly self-explanatory, but if you need a starting point here are a couple of videos. Remember, it can be digital or analogue . . . so yes, you can just use scissors, glue and any images from anywhere you can find them.
Good luck!
😀
2 To develop your production work, please find a non-copyright / copyright free piece of MUSIC (look this term up if you don’t fully understand it) that connects to your moodboard. Put another way: find a song that you can make a video to. The song needs to be related to the themes: isolation, diaspora, double consciousness, identity, self. AND needs to connect to your storyboard. Remember it also needs to feature headphones.
3 Upload this piece of music to the blog – look at the embed options, in the block types. Please avoid pasting in a link (if you can 😊).
By now you should have:
- An idea based on a theme (held in your imagination)
- A number of ‘found’ images that give you a sense of place, character, colour, size, shape, texture (held on the blog)
- A song that connects 1 & 2 together (held on the blog)
If not. There is no shortcut, so please get this done!
If so . . . move on . . .

