- COLONIALISM – When a country takes control over another country.
- POST COLONIALISM – Studying something in a colonized country.
- DIASPORA – the dispersion or spread of people from their homeland.
- BAME – UK slang that refers to minorities (asian, hispanic etc).
- DOUBLE CONSCIOUSNESS (GILROY) – Internal conflict by subordinated groups in an oppressive society.
- CULTURAL ABSOLUTISM / RACIAL ESSENTIALISM – a belief in a genetic essence that defines all members in racial categories.
- CULTURAL SYNCRETISM – Different cultures merging together to make something new.
- ORIENTALISM (SAID) – How we view Arab countries.
- APPROPRIATION – When something sacred to someone is sexualised or made fun of (e.g. native indians of america and their culture appropriated for childrens costumes on halloween).
- CULTURAL HEGEMONY – The domination of a culturally diverse society by the most popular class
- THE PUBLIC SPHERE (HABERMAS) – An area in social life where individuals can come together to freely discuss and identify societal problems, and through that discussion influence political action.
- THE ROLE OF PUBLIC SERVICE BROADCASTING IN TERMS OF FAIR REPRESENTATION OF MINORITY GROUPS / INTERESTS – These public service broadcasting groups (PBS) are mostly biased when representing ethnic minority groups which can make society adopt stereotypes and misunderstandings of these ethnic minorities.
Daily Archives: 05/13/2020
Filters
POST-COLONIALISM
COLONIALISM: Colonialism is when a country seeking to extend or keep its power and authority over other people as well as territories, generally with the aim of economic dominance. when in the process of colonisation the colonisers may introduce their own religion, economics, and other cultural practices on indigenous peoples and try to set it as the new norm.
POST-COLONIALISM: Post-colonialism is an academic discipline which includes methods of intellectual discourse that use to analyze, explain, and respond to the cultural legacies of colonialism and of imperialism as well as the human consequences that come from controlling a country and establishing settlers for the economic exploitation of the native people.
DIASPORA: it is when a scattered population who originally came from a different geographic locale. When we look at it historically, the word diaspora was used to refer to the involuntary mass dispersion of a population from its original indigenous territories, for example, the dispersion of Jews from Egypt when they had to wander the desert for 40 years to escape enslavement from the Egyptians.
BAME: is a name that refers to Black, Asian and the minority community
DOUBLE CONSCIOUSNESS (GILROY): it is a term to describe the internal conflict experienced by subordinated or colonized groups in an oppressive society.
CULTURAL ABSOLUTISM / RACIAL ESSENTIALISM: Cultural Absolutism is the ideology that there are certain principles and sets of values that are objectively right or wrong in every context and according to cultural absolutism when we consider things universally it is considered free from cultural, historical, and social conditions. racial essentialism when looking at is as a belief in a genetic or biological sense which defines all members of a racial category.
CULTURAL SYNCRETISM: is when distinct parts of different cultures combine together to create something new. Culture is a wide category so blending can come in many forms, like the form of religious practices, architecture, philosophy, recreation, and even food.
ORIENTALISM (SAID): is the acceptance in the West of “the basic distinction between East and West as the starting point for elaborate theories, epics, novels, social descriptions, and political accounts concerning the Orient, its people, customs, mind, destiny etc.
APPROPRIATION: is when you take something like ideas, customs, or a style from a group or culture that you are not a member of and to then apply it to yourself.
CULTURAL HEGEMONY: domination or rule that is maintained through ideological or cultural means. It is mainly achieved through social institutions, which means those in power can strongly influence the values, norms, ideas, expectations, worldview, and behaviour of the rest of society.
THE PUBLIC SPHERE (HABERMAS): it is a safe place for people to talk about the government.
THE ROLE OF PUBLIC SERVICE BROADCASTING IN TERMS OF FAIR REPRESENTATION OF MINORITY GROUPS / INTERESTS: their role was to reflect various community interests and news, as well as different ethnicities and cultural backgrounds to be all-inclusive to the audience.
12 definitions (POST-COLONIALISM)
- COLONIALISM-Occurs when a country or a nation takes control of other lands, regions, or territories outside of its borders (boundaries of the country) by turning those other lands, regions, or territories into a colony. Sometimes the words “colonialism” and “imperialism” are used to mean the same thing.
- POST COLONIALISM-Is the academic study of the cultural legacy of colonialism and imperialism, focusing on the human consequences of the control and exploitation of colonised people and their lands.
- DIASPORA-A diaspora is a large group of people with a similar heritage or homeland who have since moved out to places all over the world.
- BAME-Is a term long used in the UK to refer to black, Asian and minority ethnic people. Its origin derives from “political blackness”. An idea that various ethnic groups united behind to fight against discrimination in the 1970s. Now, more than 7.6 million people in Britain come under this category.
- DOUBLE CONSCIOUSNESS (GILROY)-Double consciousness is a term describing the internal conflict experienced by subordinated or colonised groups in an oppressive society. It was coined by W. E. B.(William Edward Burghardt)
- CULTURAL ABSOLUTISM / RACIAL ESSENTIALISM-According to Berry, Poortinga, Segall, and Dasen (1992), cultural absolutism is the idea that psychological phenomena, such as intelligence and honesty, do not differ from culture to culture: They are the same among cultures. The literature commonly defines racial essentialism as a belief in a genetic or biological essence that defines all members of a racial category.
- CULTURAL SYNCRETISM-Is when distinct aspects of different cultures blend together to make something new and unique. Since culture is a wide category, this blending can come in the form of religious practices, architecture, philosophy, recreation, and even food. It’s an important part of your culture.
- ORIENTALISM (SAID)-Refers to the Orient, in reference and opposition to the Occident; the East and the West, respectively. Edward Said said that Orientalism “enables the political, economic, cultural and social domination of the West, not just during colonial times, but also in the present.”
- APPROPRIATION-The act of taking something such as an idea, custom, or style from a group or culture that you are not a member of and using it yourself: Theft is the dishonest appropriation of another person’s property
- CULTURAL HEGEMONY-Cultural hegemony refers to domination or rule maintained through ideological or cultural means. It is usually achieved through social institutions, which allow those in power to strongly influence the values, norms, ideas, expectations, worldview, and behavior of the rest of society.
- THE PUBLIC SPHERE (HABERMAS)-Jürgen Habermas says, “We call events and occasions ‘public’ when they are open to all, in contrast to closed or exclusive affairs”. Jürgen Habermas defines ”the public sphere’ as a realm of our social life in which something approaching public opinion can be formed. Access is guaranteed to all citizens”.
- THE ROLE OF PUBLIC SERVICE BROADCASTING IN TERMS OF FAIR REPRESENTATION OF MINORITY GROUPS / INTERESTS– P.S.B’s role is to reflect multiple community interests and news, and different ethnicities and cultural background. to be all inclusive to there listeners.



A2 Production Work – Now Thats What I Call Quarantine
– MoodBoard(s) –
Locations –

People/ Characters –

Objects –
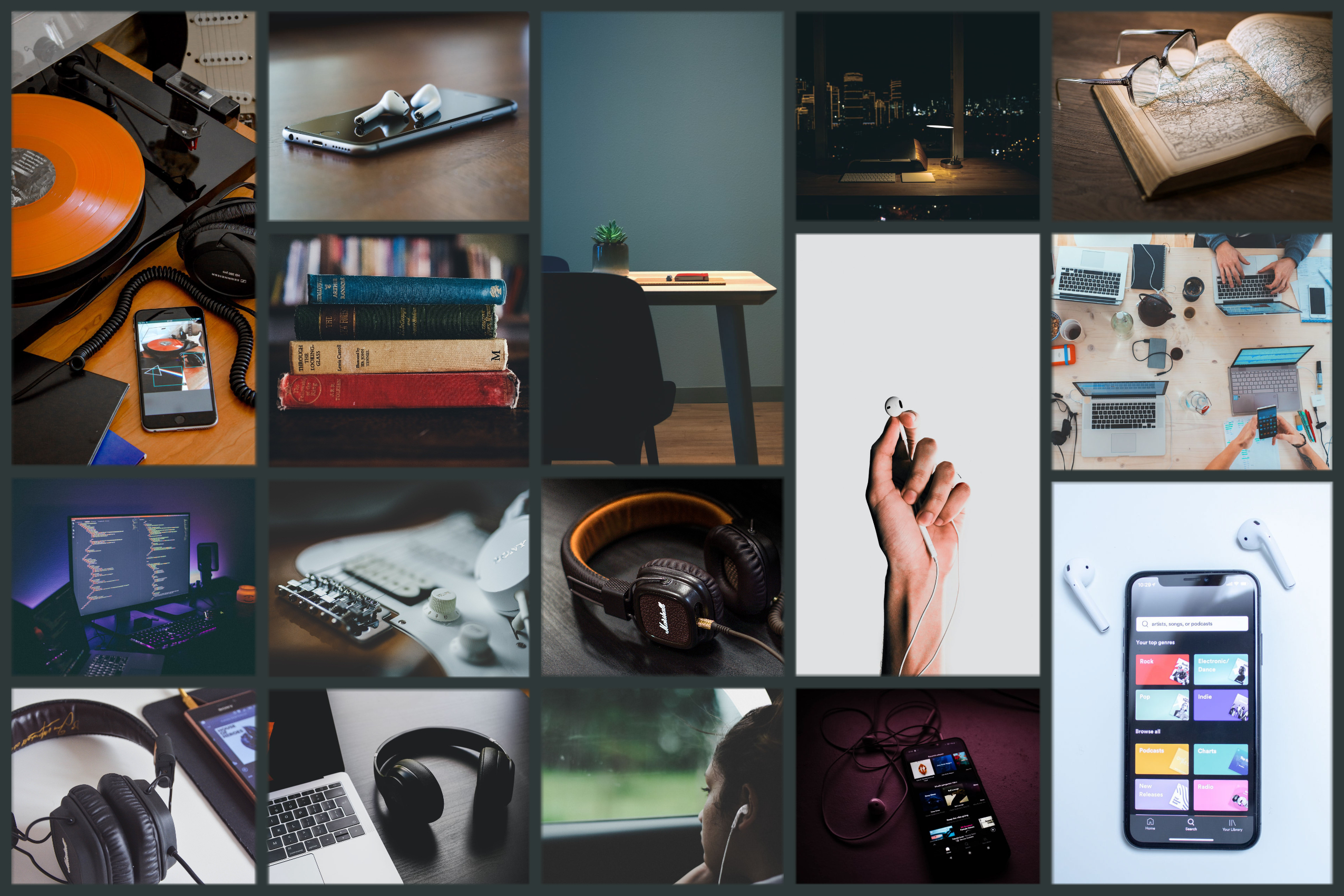

Copyright Free Music –
Image Drafts – Characters + Locations
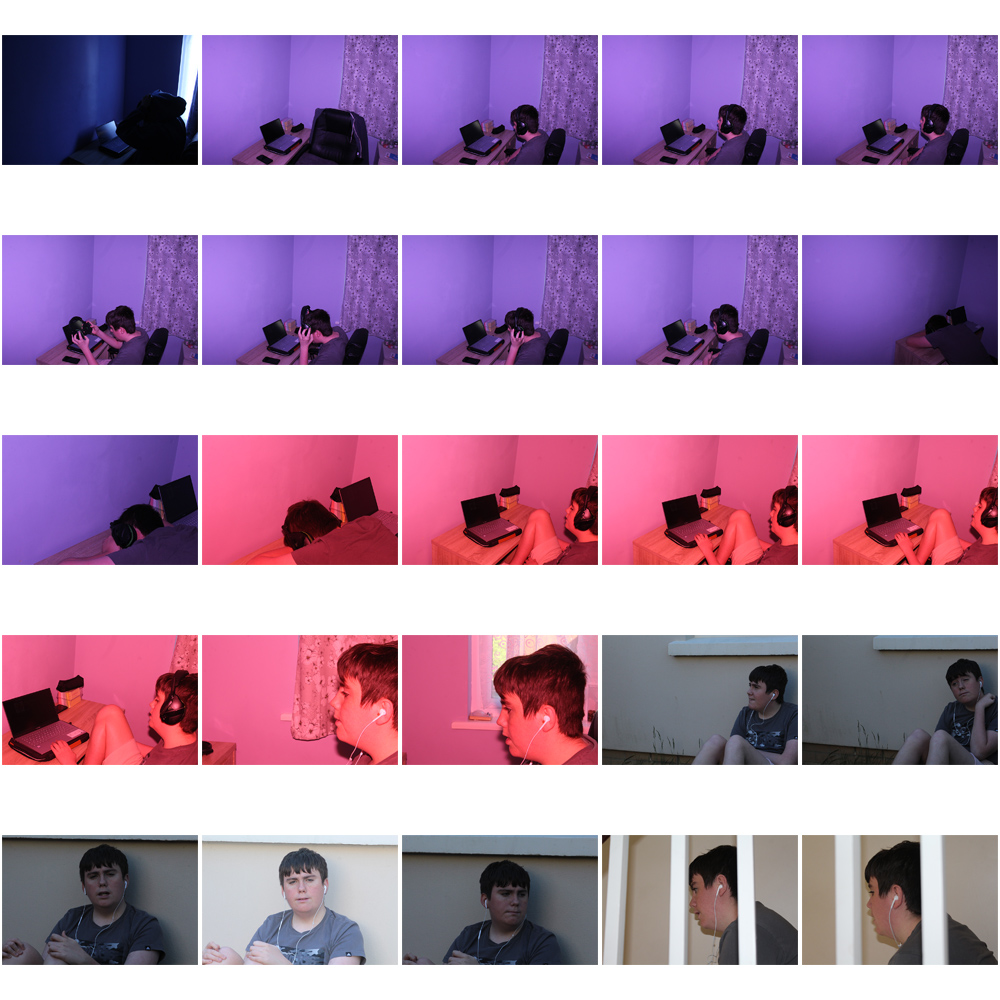

Style Models
Lana Del Rey – Summertime Sadness Analysis –
Narrative theorists to apply =
This video depicts a tragedy where one woman (played by Lana Del Rey) jumps and the other, heartbroken, follows. Todorov can be applied to this video as the start of the relationship would be the equilibirum, the breakup would be the distruption, their suicide would be their ‘resolution’ and the new equalibrium would be that they are both gone/ together again. expressed through the lyrics –
‘Got my bad baby by my heavenly side’ ‘I know if I go, I’ll die happy tonight’
‘Summertime sadness’ refers to seasonal depression that most commonly occurs in winter. However, the artist uses summer as the warmth of summer brings back memories of her lover.
Levi-Strauss theory of binary opposition can also be applied due to themes such as Love VS Hate, Life VS Death and Happy VS sad being represented throughout the video.
Although the video follows Todorovs theory of equilibrium it is not chronological as it shows multiple flashbacks. The old/ vintage film effect is used to convey the memories/ flashbacks as her own personal movie.
Coldplay – Midnight Analysis –
Narrative theorists to apply =
Levi-Strauss = Binary opposition theory can be applied to the visual elements of the video as it was shot in a negative exposure. This theory can also be applied to the lyrics ‘When I’m rolling with the thunder but bleeding from the thorns’ which is a metaphor for ‘there will always be negative for the positives’ .
‘In the swirling swimming on’ – Here, Martin’s voice rises in to match the songs content, suggesting a rising storm. The alliteration, “swirling swimming” also creates a crescendo effect similar to a storm.
The video was shot in negative exposure (Inverse)
Cavetown – Pigeon Analysis –
Narrative theorists to apply =
Beginning = Low depth of field
‘Circling around the kitchen, why has nothing changed’ refers to doing something over and over again can lead to insanity. This song shows what heartache can do to a person, however, unlike summertime sadness the final equilibrium of this video/ narrative shows that he’s still trying to bargain for his loved one back, but finally at the end of the song he accepts that they can’t come back, but he’ll try to keep going to make him proud; emphasized through the lyrics –
‘Don’t know how I’m going to live without’ ‘But I’ll stay strong for you’
Therefore, Todorovs theory of equilibrium can be applied to this narrative as well as Levi-Strauss’s binary opposition due to themes such as Love VS Hate and Sanity VS Insanity that are represented throughout.
Statement of Intent for Music Video Project –
For my music video project, I plan on using Adobe After Effects in order to create a vintage/ grain film effect which will emphasize the coloured memory shots (due to contrast). These coloured memories will be a juxtaposition against the black and white present scenes; a symbolic sign for loneliness and sadness to show how dull ‘life’ now is.
After Effects will allow me to edit each individual layer of film I have as well as combining it with other layers and sounds to achieve my desired outcome. In addition, unlike other editing software such as iMovie, After Effects allows a much more free approach at editing my different layers, their speeds and times all individually; whilst allowing me to edit at my own speed as I can adjust the speed at which the video renders and upload at a variety of different frame rates and sizes.
For the key conventions of my music video, I am going to transition between frames/scenes on the beats of the song which will therefore blend the video and the sound together. My narrative will be based upon a male solo artist, the video won’t be in chronological order as the disordered scenes (flashbacks) will allow connotations of insanity, loneliness and isolation to be created especially as there is only one character throughout.
Dominant ideology suggests that people who tend to be more ‘isolated’ or ‘lonely’ are ‘weird’; therefore, my music video will act as a radical narrative against this view as although the artists is upset, music is a thing that helps heal and bring people together.
The action code which will begin the plot/ storyline of the video will be the artist covering the camera with his hand. This section will be in colour as it is one of the memories. In addition, this camera angle will also put the viewers in first person as if they are being directly addressed by the artist. I decided to create a stage name for the artist, ‘Solum’, which is Latin for ‘alone’.
As well as this, throughout the video there will be short clips of a plain black background with some white text expressing some of the details of the tour. In order to continue the vintage theme, I plan on using the ‘Times New Roman Font’ as the serif style of it is quite vintage.
My inspirations for these techniques came from 3 different music videos – Lana Del Rey’s ‘Summertime Sadness’, Coldplay’s ‘Midnight’ and Cavetown’s ‘Pigeon’. All these videos have editing techniques such as ‘negative exposure’ which allow connotations such as darkness and coldness to be conveyed. I chose these videos as they all express a similar theme and message of anger and insanity due to the loss of something close.
Overall, my video is intended to promote the new artist by building a relationship with the audience by targeting things we can all relate to – memories or the loss of something or someone we loved.
adverts final draft 1



ISOLATION MUSIC VIDEO MOOD BOARD
Settings Mood board:

Characters Mood board:

Props Mood board:

Music
post colonialism
- Colonialism – a policy of acquiring full or partial political control over another country
- Post Colonialism – theoretical approach in multiple different disciplines
- Diaspora – dispersion of any people that are from their original homeland
- Bame – a term that has been used in the UK to refer to black or people of a different ethnicity
- Double consciousness (Gilroy) – a book about the black atlantic culture that has incorporated elements from different cultures e.g. African, American, British and Caribbean
- Cultural absolutism – the idea created exploiting that there are certain principles and sets of values that are either right or wrong in every context
- Cultural syncretism – distinct aspects of different cultures are combined together to create something new and unique
- Orientalism – a book written by Edward W Said, in which he developed the complete idea of Orientalism to define the West’s historic representation of The East
- Appropriation – where a culture adopts different aspects of another culture
- Cultural hegemony – domination or power maintained by ideological or cultural meanings
- The public sphere – a gained public opinion obtained that can be formed about the activities taken place within the government
- The role of public service broadcasting – for example the BBC news are usually biased towards different minorities in a negative manner portraying an unfair image of how they’re presented
post colonialism definitions
COLONIALISM – the policy or practice of acquiring full or partial political control over another country, occupying it with settlers, and exploiting it economically.
POST COLONIALISM – Postcolonialism is the academic study of the cultural legacy of colonialism and imperialism, focusing on the human consequences of the control and exploitation of colonized people and their lands.
DIASPORA – A diaspora is a scattered population whose origin lies in a separate geographic locale.
BAME – BAME is a term long used in the UK to refer to black, Asian and minority ethnic people.
DOUBLE CONSCIOUSNESS (GILROY) – a history book about a distinct black Atlantic culture that incorporated elements from African, American, British, and Caribbean cultures. Written by paul gilroy
CULTURAL ABSOLUTISM / RACIAL ESSENTIALISM – Cultural Absolutism is the idea that there are certain principles and sets of values that are objectively right or wrong in every context. Racial essentialism is as a belief in a genetic or biological essence that defines all members of a racial category
CULTURAL SYNCRETISM – Cultural syncretism is when distinct aspects of different cultures blend together to make something new and unique.
ORIENTALISM (SAID) – Orientalism is a book by Edward W. Said, in which the author developed the idea of “Orientalism” to define the West’s historically patronizing representations of “The East”
APPROPRIATION – is the adoption of an element or elements of one culture by members of another culture.
CULTURAL HEGEMONY – cultural hegemony is the domination of a culturally diverse society by the ruling class who manipulate the culture of that society
THE PUBLIC SPHERE (HABERMAS) – the public sphere is an area in social life where individuals can come together to freely discuss and identify societal problems, and through that discussion influence political action.
postcolonialism
- COLONIALISM – taking full or partial political control of another country
- POST COLONIALISM – academic study of colonialism and imperialism focusing on human consequences
- DIASPORA – dispersion of people living outside of their homeland
- BAME – minorities eg black/asian people
- DOUBLE CONSCIOUSNESS (GILROY) – internal conflict between subordinated groups in an oppressive society
- CULTURAL ABSOLUTISM / RACIAL ESSENTIALISM – assumption that someone’s cultural values are more important than others
- CULTURAL SYNCRETISM – different cultures come together to create something new positively
- ORIENTALISM (SAID) – how the middle east is viewed
- APPROPRIATION – a culture adopts parts of another culture
- CULTURAL HEGEMONY – domination (power) maintained by ideological or cultural means
- THE PUBLIC SPHERE (HABERMAS) – a public opinion can be formed about government activities
- THE ROLE OF PUBLIC SERVICE BROADCASTING IN TERMS OF FAIR REPRESENTATION OF MINORITY GROUPS / INTERESTS – eg BBC, tyhe news is usually biased and acts negatively towards minorities which creates an unfair image of them
