- BOOK – modernity and self identity
- “in modern social life, the notion of lifestyle takes on a particualr significance”
- “the more tradition loses its hold, people are forced to negotiate lifestyle choices”
- “lifestyle choice is increasingly important in the construction of self-identity”
- “reflexively organised life planning is a central feature of structuring identity”
Monthly Archives: February 2020
Filters
Gauntlett – representations
Popular media present a vast array of stories about women and men.
The new edition of Media, Gender and Identity is a highly readable introduction to the relationship between media and gender identities today. Fully revised and updated, including new case studies and a new chapter, it considers a wide range of research and provides new ways for thinking about the media’s influence on gender and sexuality.
David Gauntlett discusses movies such as Knocked Up and Spiderman 3, men’s and women’s magazines, TV shows, self-help books, YouTube videos, and more, to show how the media play a role in the shaping of individual self-identities.
Gauntlett
‘most men and women remain somewhat constricted within particular gender roles’
book – making is connecting – ‘how people build self identity through creative practices’ (connect to a piece of media by creating their own ideologies)
Representation/ Audience Theory
plural Identity –
The presence of more than one identity in a piece of media. E.G in CSP3 there is vin diesel + a 69 year old man – different identities.
Uses and Gratifications Theory –
- information + education
- escapism
- entertainment
- personal identity
- social interaction
Active Audience not passive – the audience decide what media they want to view.
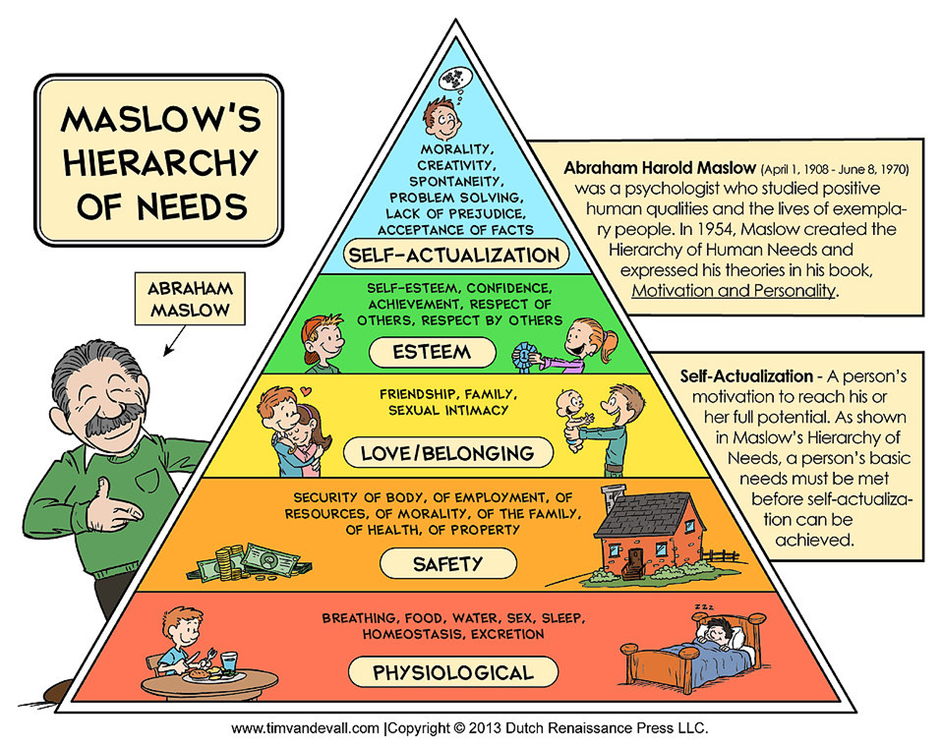
Uses and Gratifications in relation to Maslows theory –
Different groups from the Uses and Gratifications theory relates to the different heirarchies of Maslows pyramid.
By categorizing the audience’s motives for viewing a certain program into certain groups (Information and education, Escapism, Entertainment, Personal identity and Social Interaction) they aimed to classify viewers according to their needs (Maslows heiracrchy of needs) in order to understand any potential mass-media effects.
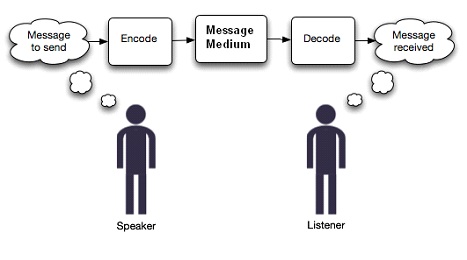
Stuart Hall – Theory of Preffered Reading (Encode/Decode Model)
Presented the ide that the way others, due to that time generally white males, interpret media is going to be very different to the way stuwart halls community interprets media.
Meaning is created from the interpretations of the reader, not necessarilt what the author/ creater intended.
Narrative and Genre Theory –
• Narrative Codes
• Narration
• Diegesis
• Quest narrative
• ‘Character types’
• Causality
• Plot
• Masterplot
Todorov (Tripartite narrative structure):
• Equilibrium
• Disruption
• New equilibrium
Seymour Chatman:
- Kernels: key moments in the plot / narrative structure
- Satellites: embellishments, developments, aesthetics
Roland Barthes: Proairetic and Hermenuetic Codes
- Proairetic code: action, movement, causation
- Hermenuetic code: reflection, dialogue, character or thematic development
Vladimir Propp (Character Types and Function)
- Hero
- Villain
- Victim
- Princess
- Dispatcher
- False Hero
- Father
- The villain. struggles against the hero.
- The donor. prepares the hero or gives the hero some magical object.
- The (magical) helper. helps the hero in the quest.
- The princess and her father. …
- The dispatcher. …
- The hero or victim/seeker hero. …
- False hero
GENRE THEORY
Uses & gratifications/Audience Theory

DEMOGRAPHIC/PSYCHOGRAPHIC CLASSIFICATION:
Demographic: A socio-economic classification developed by the NRS (National Readership Survey)
Psychographic: A Psychographic Model of consumer behaviour used in the media industry to define audience segments.
Links into Maslows theory!
Stuart haul: reception theory, theory of preferred reading, encode decode
revision
Katz+blumler
The Blumler & Katz theory is the understanding of what the audience does for the media not what the media does for the audience. It is the integration that the audience does for the media that helps sales, for example, buying of the product
Uses and gratifications
Uses and gratifications theory (UGTtheory) is an approach to understanding why and how people actively seek out specific media to satisfy specific needs. UGT is an audience-centred approach to understanding mass communication, Unlike many media theories that view media users as passive, uses and gratifications sees users as active agents who have control over their media consumption
semiotics revision
paradigm – example, model, standard
theorists
ronald barthes – myths
saussure – signs and signifiers
c s pierce –
THEORIES OF REPRESENTATION

Quotes from Modernity and Self Identity: Self and Society in the Late Modern Age (Anthony Giddens)
- Yet because of the “openness” of social life today, the pluralization of contexts of action and diversity of “authorities”, lifestyle choices is increasingly important in the constitution of self identity and daily activity.
- In modern social life, the notion of lifestyle takes on a a particular significance
- Reflexively organised life planning, which normally presumes consideration of risks, as filtered through contact with expert knowledge, becomes a central feature of the structuring of self identity.
- Which consists in the sustaining of coherent, yet continuously revised, biographical narratives, takes place in the context of multiple choice as filtered through abstract systems.
Anthony Giddens
Giddens structuration theory
Giddens argues that just as an individual’s autonomy is influenced by structure, structures are maintained and adapted through the exercise of agency so structuration theory attempts to understand human social behaviour by resolving the competing views of structure-agency and macro-micro perspectives.
The structure is the recurrent patterned arrangements which influence or limit the choices and opportunities available. Agency is the capacity of individuals to act independently and to make their own free choices.
A macro perspective is basically looking at the bigger picture of things as a whole. A micro-perspective is taking a “deeper dive” and looking at the specifics of things.
