Todorov – Order = Beginning, Middle and End – Narrative Structure
Levi-Strauss – Binary Opposition = Love VS Evil
Propp = 8 stock character types all narratives contain e.g princess, hero, villain.
Todorov – Order = Beginning, Middle and End – Narrative Structure
Levi-Strauss – Binary Opposition = Love VS Evil
Propp = 8 stock character types all narratives contain e.g princess, hero, villain.

For many, the wider social, political, historical and cultural contexts are not just clearly connected to media studies but they are in some ways more important.
“I’ve always said you can’t understand the world without the media nor the media without the world” (Professor Natalie Fenton, quoted in Fake news vs Media Studies J. McDougall p.17 2019, Palgrave)
“I do spend long periods of time with my gaze turned away from the media, because I’m seeking to understand what’s going on out there, and then the role of the media in that context. I’m always putting the social, the political and the economic (contexts) first.” (ibid)



War of the Worlds can be considered in a historical context as it provides an interesting study of the power and influence of radio as a form during its early days of broadcasting. It is also useful to consider the product in a social, cultural and political context when considering audience responses to the programme. It was first broadcast on the eve of World War II and reflected fears of invasion in the US and concerns about international relations.
Letter to the Free is a product which possesses cultural and social significance. It will invite comparison with other music videos allowing for an analysis of the contexts in which they are produced and consumed. Common is an Oscar and Grammy award winning hip/hop rap artist who wrote Letter to the Free as a soundtrack to The 13th – a documentary by Ava DuVernay named after the American 13th amendment (the abolition of slavery). His output is highly politicised, existing in the context of a variety of social and cultural movements aimed at raising awareness of racism and its effects in US society (e.g.: Black Lives Matter). The product can also be considered in an economic context through the consideration of if and how music videos make money (through, for example, advertising on YouTube).
Hidden Figures is a Hollywood low to medium budget film which combines serious (potentially controversial) themes about race in the US with a familiar, accessible film style.
Hidden Figures deals with US history and the idea of the contribution of particular groups being ‘hidden from history’ (apparent in the marketing of the film). The subject matter of the film also links to contemporary concerns and debates about race in the US. The film is also targeted at an audience often ignored by Hollywood due to age, gender and race and thus can be explored in terms of the social and cultural context in which it was produced. As a low to medium budget film, it will be interesting to consider this film in its economic context, especially in comparison to big-budget Hollywood films.
The maybelline campaign engages with contemporary debates around ‘identity’ and ‘the self’ – in particular, the notion of a reflexive, fluid identity that is symptomatic of the role that contemporary digital media plays in the era of ‘modernity’, articulated and discussed in the work of both David Gauntlett and Anthony Giddens.
Read this extract from a book called Modernity and Self Identity: Self and Society in the Late Modern Age, written by Anthony Giddens. Or look up some quotes by Gauntlett that help you to both understand and express these ideas.

here is an edited version:
“The reflexive project of the self, which consists of the sustaining of consistent, yet continuously revised, biographical narratives, takes place in the context of multiple choice as filtered through abstract systems. In modern social life, the notion of lifestyle takes on a particular significance. The more tradition loses it hold, and the more daily life is reconstituted . . . the more individuals are forced to negotiate lifestyle choices among a diversity of options. Of course there are standardising influences . . . Yet because of the ‘openess’ of social life today, the pluralisation of contexts of action and the diversity of ‘authorities’, lifestyle choice is increasingly important in the constitution of self-identity and daily activity.”
Can you translate some of his ideas? For example, what is reflexivity? If you need more help you can read this post from my own blog: Representation, Identity & Self
Ayesha Tan Jones is a non-binary artist and musician who goes by the stage name ‘YaYaBones’
Once you have thought about this, think about the concept of a ‘non binary identity’. Follow this link to find out more. What does this mean to you? How do you feel about it? What about the concept of CIS? Or Intersex?
Do these concepts help you to understand the idea behind the Maybelline marketing campaign?
Again discuss this with your group of friends, make notes and be prepared to feedback to the rest of the class.
So how is the traditional male representation adjusting to this new world from the perspective of Advertising & Marketing?
stuart hall – encode -> decode
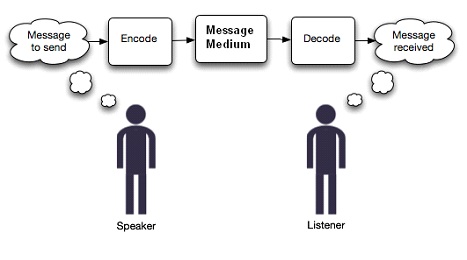
stuart hall – reception theory
two step flow model:

by paul lazarfield
To what extent do television producers attempt to target national and global audiences and subject matter and distribution?
the missing & AUDIENCE THEORY
Media Language:
Representations:
Industries:
Audiences:
With reference to Witnesses (Les Temoins, France) and The Missing (UK).
Witnesses (Les Temoins, France):
hyperreality – the inability to distinguish between fiction and fact (hyper-realism) – the missing
The Missing (UK):
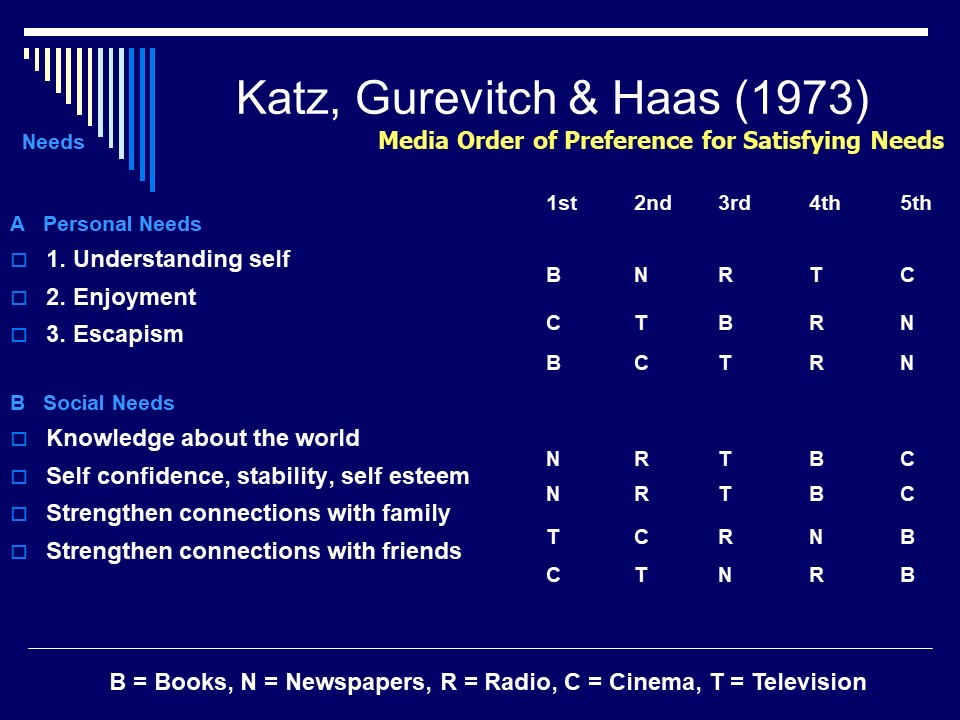
Katz, Gurevitch and Haas: Audiences experience media to fulfill needs and gratifications. They can be personal needs, like understanding self, escapism or enjoyment. They can also be social needs, like connecting with friends and family, knowledge of the world,Self confidence, stability.
Psychographics:

Hans, Gurevitch and Katz (1973)
The theory is that there are two different needs of the public: Personal needs and Social Needs.
Personal needs are for a specific individual. These can be for one to understand themselves, Enjoyment and Escapism.
Social needs are for needs of everyone in the public who have similar views which makes them a discourse community. This can be knowledge about the world, self ability, awareness and self esteem, to strengthen bonds with family and friends.
DEMOGRAPHIC/PSYCHOGRAPHIC CLASSIFICATION:
Demographic: A socio-economic classification developed by the NRS (National Readership Survey)
Psychographic: A Psychographic Model of consumer behaviour used in the media industry to define audience segments.
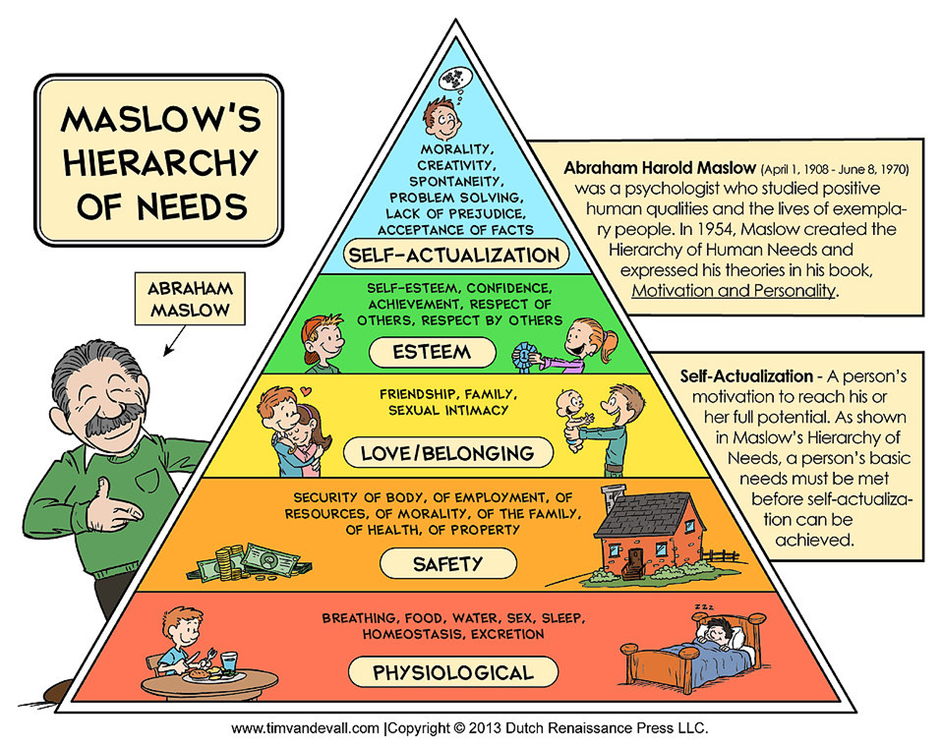
Links into Maslows theory!
Maslows Hierarchy of Needs

Demographic: A socio-economic classification developed by the NRS (National Readership Survey)
Psychographic: A Psychographic Model of consumer behaviour used in the media industry to define audience segments.
Uses and Gratifications Theory Categories –
Maslow’s Theory:
Different people can relate to different stages of hierarchy on Maslow’s pyramid, and by categorizing why different people watch certain things this helps to provide reason and an aim for people to satisfy their viewers and maybe appeal to other viewers as well. Factors such as gender, age, ethnicity etc. effect where u lie on the pyramid.
Blumler and Katz theorised that people have 5 main reasons to use media:
MASLOW’S HIERARCHY OF NEEDS
DEMOGRAPHICS AND PSYCHOGRAPHICS
Demographics: Quantitative data, age,race,ethnicity,sex
socio-economic status = A,B,C1,C2,D,E
other descriptives of demographics= Elite, Established middle class, Technical middle class, New affluent workers,Traditional working class, Emergent Service workers and the Precariat, or the precious Proletariat
Psychographics: Aspirer, Explorer, Resigned, Mainstreamer, Reformer, Succeeder, Struggler
Psychographic information might be your buyer’s habits, hobbies, spending habits and values. … Demographic information includes gender, age, income, marital status – the dry facts.
Haas, gurevitch and katz (1973)
personal needs : enjoyment, escapism, understanding self
social needs : knowledge, self confidence/esteem, strengthen connections with friends and family
stemmed from maslow’s hierarchy of needs
PSYCHOGRAPHIC
how people think about things and receive media
DEMOGRAPHIC