plural Identity –
The presence of more than one identity in a piece of media. E.G in CSP3 there is vin diesel + a 69 year old man – different identities.
Uses and Gratifications Theory –
- information + education
- escapism
- entertainment
- personal identity
- social interaction
Active Audience not passive – the audience decide what media they want to view.
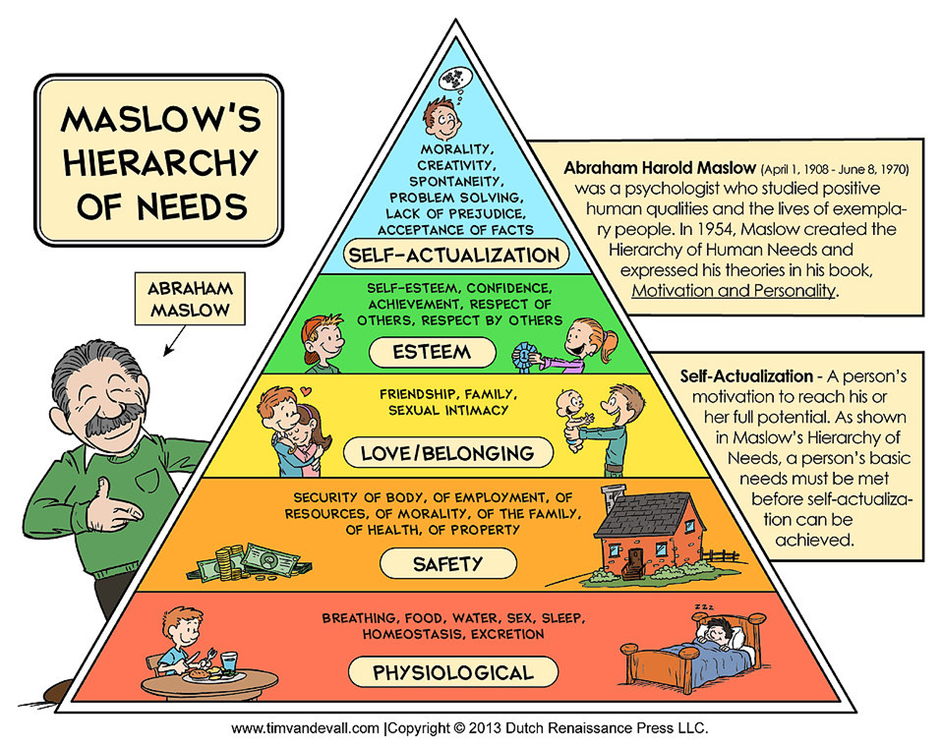
Uses and Gratifications in relation to Maslows theory –
Different groups from the Uses and Gratifications theory relates to the different heirarchies of Maslows pyramid.
By categorizing the audience’s motives for viewing a certain program into certain groups (Information and education, Escapism, Entertainment, Personal identity and Social Interaction) they aimed to classify viewers according to their needs (Maslows heiracrchy of needs) in order to understand any potential mass-media effects.
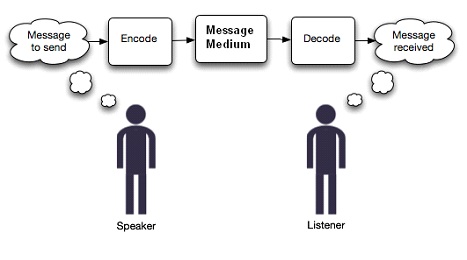
Stuart Hall – Theory of Preffered Reading (Encode/Decode Model)
Presented the ide that the way others, due to that time generally white males, interpret media is going to be very different to the way stuwart halls community interprets media.
Meaning is created from the interpretations of the reader, not necessarilt what the author/ creater intended.
Narrative and Genre Theory –
• Narrative Codes
• Narration
• Diegesis
• Quest narrative
• ‘Character types’
• Causality
• Plot
• Masterplot
Todorov (Tripartite narrative structure):
• Equilibrium
• Disruption
• New equilibrium
Seymour Chatman:
- Kernels: key moments in the plot / narrative structure
- Satellites: embellishments, developments, aesthetics
Roland Barthes: Proairetic and Hermenuetic Codes
- Proairetic code: action, movement, causation
- Hermenuetic code: reflection, dialogue, character or thematic development
Vladimir Propp (Character Types and Function)
- Hero
- Villain
- Victim
- Princess
- Dispatcher
- False Hero
- Father
- The villain. struggles against the hero.
- The donor. prepares the hero or gives the hero some magical object.
- The (magical) helper. helps the hero in the quest.
- The princess and her father. …
- The dispatcher. …
- The hero or victim/seeker hero. …
- False hero
GENRE THEORY