| Category | Familiarities | differences | theory |
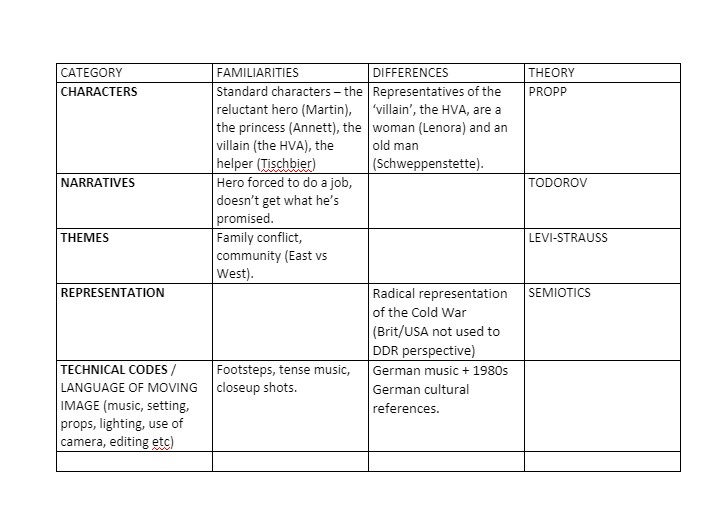
| characters | clear and obvious protagonist that will conflict the danger head on with a clear enemy or antagonist being western society. | they have an instinct engraved into their society that they must give up their life to please the government your life and repay your debt of them raising you and that your body belongs to them so they choose what happens to it. | propp |
| narrative | The protagonist is being made to do something that he/she doesn’t want to do but must be done for the greater good of their state and country. | The protagonist starts off with power when he tells the people off for smuggling Shakespeare into their country which is contraband. His power is then taken away when he meets people superior to him as they tell him to go away as a spy and complete a spy mission. | todorov |
| themes | secrets and lies are kept from the population to keep people from the truth as it might make them look bad. | the secrets are being exposed through dramatic irony that the viewers already know | Levi Strauss |
| representation | One nation or opposition is classified or represented as evil and a danger to their way of living | the difference is that our standard of living is the evil one. | semiotics |
| technical codes | music is being played In German on the radio which is similar to what we do | the difference is that they are playing foreign music unlike us because we wouldn’t play foreign music often. |
Daily Archives: 11/15/2019
Filters
Deutschland
| Category | Familiarities | Differences | Theory |
| Characters | Propp | ||
| Narrative | Todorov | ||
| Themes | Levi Strauss | ||
| Representation | Semiotics | ||
| Technical Codes | The character was sweaty |
deutschland 83 table
similaraties and differences between english and german shows
Similarities:
chase scene: we expected the character to be caught
the protagonist was immediately introduced as the chosen one
we expected him to be nearly caught taking the photos
we expected him to try make contact with loved ones because its an instinct
when the lock is being picked the sound increases
Differences:
Language
Set in enemy territory showing their point of view.
Define key terms
Define each of these key terms
- Repertoire of elements – Characters. covers the theory that a certain genre of film will have similar characters. In a crime film there will often be the Italian mobster. Setting. covers the idea that the same genre of film will have similar settings.
- Corpus – a collection of written or spoken language data in a computer-readable format. It brings together large quantities of language evidence from a variety of real situations which lexicographers use to compile accurate and meaningful dictionary entries.
- Hybridisation – Hybridization is a term used to describe a type of media convergence whereby a new mode emerges containing elements of combined media. Hybrid media represent most modern media and the concept that different media forms can work together to create new media.
- Historic specificity –
- Repetition and Sameness
- Variation and change
- Narrative image
- Expectations and hypotheses
- Suspend disbelief
- Generic regime of verisimilitude
Stephen Neale’s Genre Theory Definitions
Stephen Neale – Prominent UK-based film theorist who has made an enormous contribution to the field of genre studies
Repertoire of elements – Repeated features that are identical and recognisable as a specif genre eg horror = dark, jump scares, night, groups of people
Corpus – Genres evolve as new texts and are added to the body of similar texts
Hybridisation – The merging of different genres to create a sub-genre , more than one genre in a text
Historic specificity – They are associated with certain time periods and tend to have been popular at a particular moment in time due to other cultural, economic or historical factors
Repetition and sameness – Genre text producers have a fine line between repeating successful formulas with only minor variations
Variation and change – Varying the genre sufficiently to still allow familiarity but also make the audience feel the product they are consuming seems fresh
Narrative image – Tells a story through moving image, and closely follows a narrative structure to similar texts in that genre
Expectations and hypotheses – Audiences like to predict what’s going to happen, eg in a horror film you can tell when something’s going to happen like a jump scare because they music builds up or it’s silent and the camera’s moving rapidly between shots
Suspend disbelief – The audience needs to care about the characters in order for them to remain interested in the text this can be done by making them think a certain thing may happen (audience positioning)
Generic regime of verisimilitude – Making things very similar and match up to both our experience of other texts and of the real world so they’re believable
Conventions and rules – There are certain rules / structures / features that need to be included in a text to make it a certain genre
Sub-genre – A genre that has derived from the original main genre but doesn’t contain all of the required features and can have differences to this as well
Hybridity – Putting 2 or more different things together
definitions
repertoire of elements- key elements of a film that are consistently repeated throughout a genre.
hybridization- merging and combining different elements of media together.
corpus- when genres evolve as new texts are added to the body of similar texts.
historic specificity- genres that are associated with certain specific time periods.
repetition and sameness- the action of repeating something and something being the same.
variation and change- changing something from how it is or how it has or should been.
narrative image- telling a story in the moment or how it’s going or sequence of events unfolding over time.
expectations and hypothesis- how something is expected or believed to be and as proposition made as a basis of believing.
suspend disbelief- temporarily allow someone to believe something that isn’t true, especially to enjoy a work of fiction.
generic regime of verisimilitude- refers to what is likely to happen in a genre.
Key Terms
Conventions and Rules: Media conventions are rules or generally accepted ways of combining codes to create form and meaning within a media production.
Sub-Genre: A genre that is part of a larger genre the series is part of the blooming “urban fantasy” which features super natural creatures.
Hybridity: Hybridity is to be understood as a mixture of genres in a movie or anything that involves a genre(s).
Corpus: Corpus means a collection of facts and things. Corpus is associated with storage, indexing, search and delivery of multimedia data.
Repertoire of Elements: Repertoire are key elements of a film that are consistently repeated throughout a genre. Each genre has its own repertoire of elements which elements it as that genre.
Repetition and Sameness: This means that genre text producers walk a fine line between repeating successful formulas with only minor variations.
Variation and Change:
CSP4: The Killing
Production – the process of creating a product.
Distribution – the process of sharing something to a large audience.
Exhibition – a public display of something; this is usually a piece of art.
It was set in Denmark
Producer: Søren Sveistrup
Genre: Danish Police Drama
Broadcast on: Amazon, BBC4 and Netflix
DEFINITIONS
Repertoire of elements- the theory that a certain genre of film will have similar characters
Corpus- Big structured text
Hybridisation- Is a genre that is a mix of themes and elements from two or more different genres
Historic Specificity- Associated with certain time periods
Repetition ans sameness- Genre text producers walk a fine line between repeating successful formulas with only minor variations
Variation and change- Varying it sufficiently to still allow familiarity but also make the audience feel the product they are consuming feels fresh.
Narrative image- visual story telling
Expectation and hypothesis- The assumption of the audience based on how its presented
Suspend disbelief-
