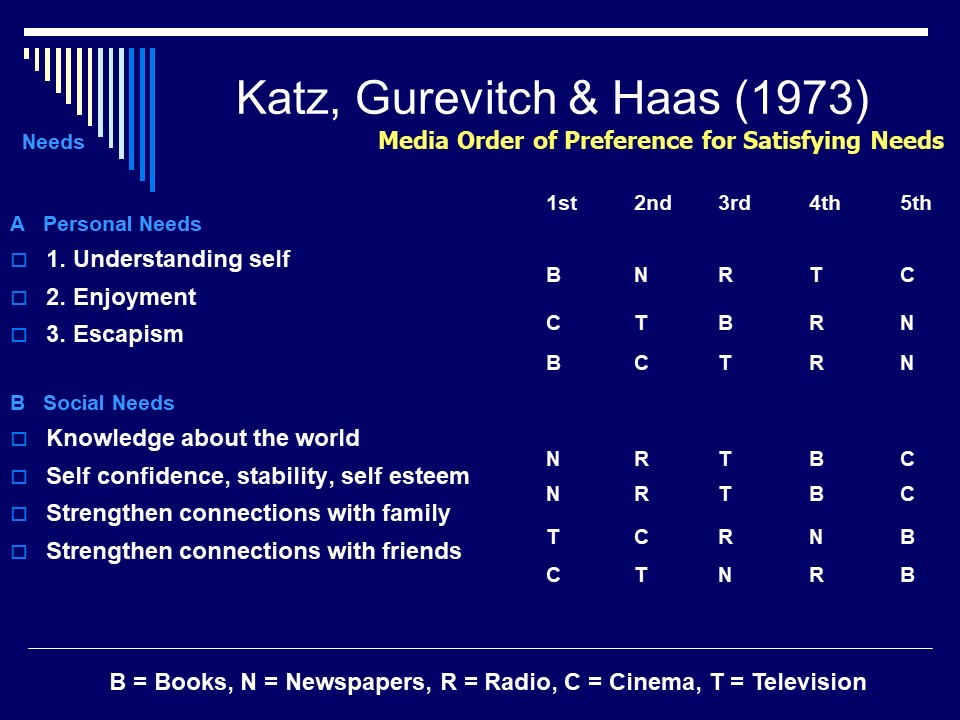
Barthes- A french philosopher who explored semiotics and social theory
Pierce- An American philosopher, logician, mathematician, and scientist who is sometimes known as “the father of pragmatism”.
Saussure – A Swiss linguist and semiotician. His ideas laid a foundation for many significant developments in both linguistics and semiology in the 20th century. He is widely considered one of the founders of 20th-century linguistics and one of two major founders of semiotics/semiology.
Semiotics – The study of sign process
Sign- A gesture or action used to convey information or an instruction.
Signifier – A signs physical form (such as a sound, printed word, or image) as distinct from its meaning ( Saussure)
Signified- the meaning or idea expressed by a sign, as distinct from the physical form in which it is expressed.
Icon- person or thing regarded as a representative symbol or as worthy of veneration.
Index- a sign or measure of something
Symbol- A symbol is a mark, sign or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship.
Code – A system of words, letters, figures, or symbols used to represent others
Dominant Signifier – Dominant meaning of sign
Anchorage – Directs the viewer to chosen meaning
Ideology – A system of ideas and ideals, especially one which forms the basis of economic or political theory and policy.
Paradigm – A typical example or pattern of something
Syntagm – the relationship is one where signs occur in sequence or parallel and operate together to create meaning
Signifcation – the representation or conveying of meaning.
Denotation – he literal or primary meaning of a word, in contrast to the feelings or ideas that the word suggests. (Bathes)
Connotation – an idea or feeling which a word invokes for a person in addition to its literal or primary meaning.” (Bathes)
Myth- Belief that isn’t true