Write up a 750 word formal essay (ie beginning, main body and conclusion) that compares the representation of gender in both Mens Health and Tomb raider (draw on all of the pages and not just the front cover). Use key language and specifically show your knowledge of: 1. SEMIOTICS, 2. PRINT LANGUAGE, 3. REPRESENTATION & 4. AUDIENCE THEORY.
GUIDANCE: Compare the specific choices that have been made in the representation of gender in the two products. In your answer, you must consider:
- how gender is represented through processes of selection and combination
- the reasons for the choices made in the representation of gender
- the similarities and differences in the representations of gender
- how far these representations are influenced by historical, social and political contexts of media.
DUE 30th OCT 9AM
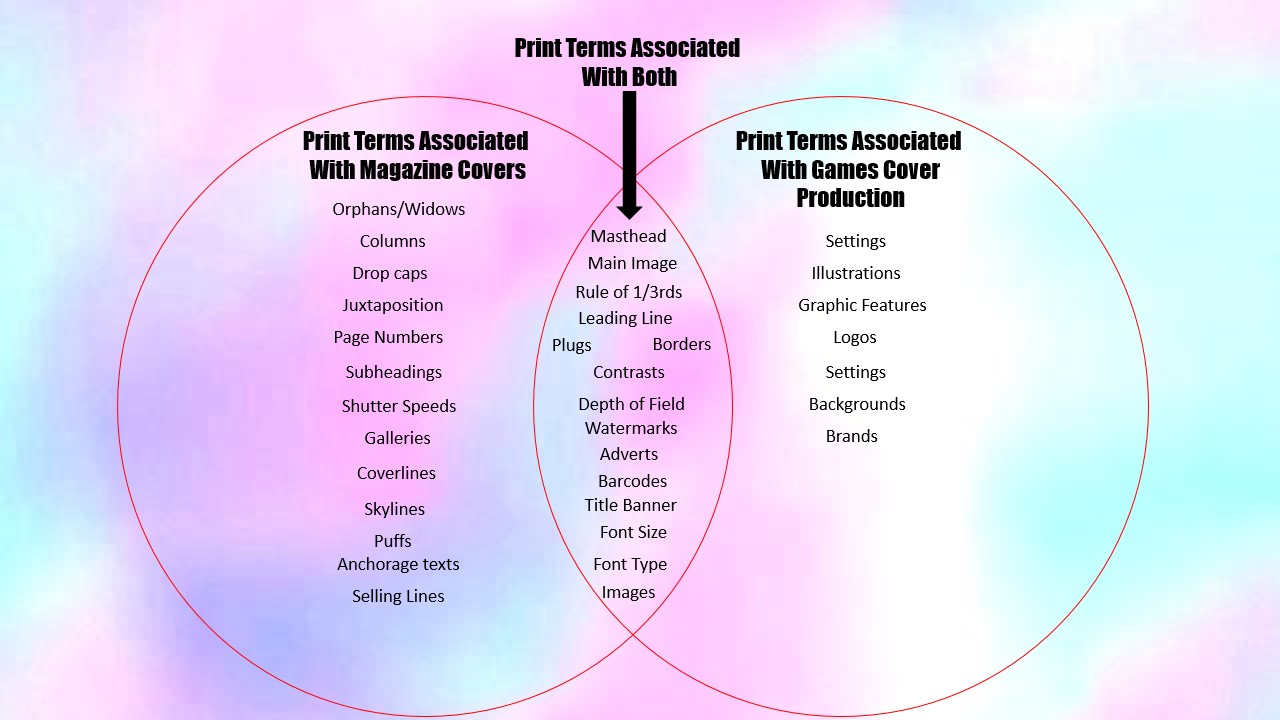
Plan:
- Females’ features are defined to show off their curves and feminine features (ie bottom and the hourglass shape of women’s bodies)
- Talk about the strategic bum covering.
- Misrepresentation = females are misrepresented by Tomb Raider as Lara Croft is holding a gun.
- Semiotics of Men’s Health and Tomb Raider
- Talk about the different audience theories (ie cultivated audience theory)
- according to a report conducted by the BBC, Lara Croft was marketed as a cyber-sex symbol, to entice more females to play the game through allowing them to play as a beautiful, female character, who is the protagonist of the “Tomb Raider” Franchise.
- According to Heather Gibson, one of the creators of Lara Croft, “The story goes that within the industry it wasn’t easy to sell a female heroine…Up until then they were quite masculine characters because your main market was men or boys.”
- Iain Simon, the founder of the GameCity festival says “I think she [Lara Croft] was part of a broader movement towards a new kind of powerful feminism that came about.”
- According to a viral tweet on Twitter, someone stated about the first-generation character of Lara Croft, “Look at the proportions. Look at the clothing. Look at the pose. They’re all sexy! Lara Croft isn’t a model. Her job is not to look sexy. She is a Tomb raider. She’s supposed to be quick, gritty and tough. Sexy is merely a bonus. But the picture says otherwise. The original Lara Croft was designed keeping her sexiness in focus. Feminists or any rational person won’t like that because they don’t like their sexiness being focussed upon and then using it as basis for their entire value Women are a lot more than just sexy. Women can be tough, intimidating, gritty, brave, funny, smart and a lot more”
My Essay Draft
Men’s Health and Tomb Raider are two sources of media that represent gender very differently. Men’s Health has a target audience of males who are into fitness, however, Tomb Raider is aimed at males, even though the conventions of a male orientated video game are broken by using a female as the protagonist. What is similar about these media sources is that they are both aimed at a target audience of young adult men, as Men’s Health only consists of images of men and Tomb Raider has a central image of a beautiful young girl, which attracts males, the target audience, to play the game.
“Men’s Health” and “Tomb Raider” represent gender very differently. Men’s Health follows the dominant ideology of males and follows the gender stereotype of males being muscular and regularly attending the gym, thus being represented as quite reactionary. However, the cover of Tomb Raider is represented as radical as the main image of Lara Croft goes against the dominant ideology of females, as shown by Lara Croft holding a gun, going against the gender stereotype of women being caring. On the Tomb Raider cover, Lara Croft’s features has been designed to show off her large bottom and hourglass body shape by positioning her sideways on, while the man on the cover of Men’s Health is standing in a pose to make him appear to be quite tough and to show off his defined muscles, thus making the central image of Men’s Health appear reactionary.
The Men’s Health magazine cover uses lots of blue and blacks, as they are colours stereotypically associated with males, however, the Tomb Raider game cover goes against the gender stereotype of females, as the cover uses oranges, blacks and greens, colours that associate with fire and adventure, which goes against the ideology of females. The mis-en-scene of the Men’s Health magazine follows the dominant ideology of males, as signified by the image of the interviewee running, which fits in with the ideology of the magazine as it is based around sports. However, the mis-en-scene used on the game cover of Tomb Raider goes against the dominant ideology of females because Lara Croft is holding a gun in front of a ring of fire, which presents her as radical, rather than reactionary. The settings of both the media sources counteract against each other because Men’s Health uses a very soft background against their images, which could be misinterpreted and seem as if males are being represented as quite feminine. Alternatively, Tomb Raider does the opposite of Men’s Health, by representing females as quite masculine and against the dominant ideology of females, as suggested by putting the central image against a dark colour and fire, which typically signify danger, thus identifying that Lara Croft goes against the regime of females.
To conclude, Men’s Health and Tomb Raider contrast in the representation of gender. This is shown by the mis-en-scene of both the central image of the products, which is reactionary as they follow the dominant ideology of what females and men aim to look like. The coloring of the media sources also represent gender very differently as Men’s Health uses colours that are stereo-typically associated with females; however, Tomb Raider goes against this by using colours associated with danger, thus going against the dominant ideology of females. The setting of the media sources also represent gender very differently, as Men’s Health uses a soft background, which is a bit misleading as it could appear quite feminine. Whereas, Lara Croft on the Tomb Raider game cover uses fire and an Egyptian style background, which also misrepresents females as it could appear quite masculine, which then presents Lara Croft as being quite masculine and a figure who goes against the dominant ideology of females in media.