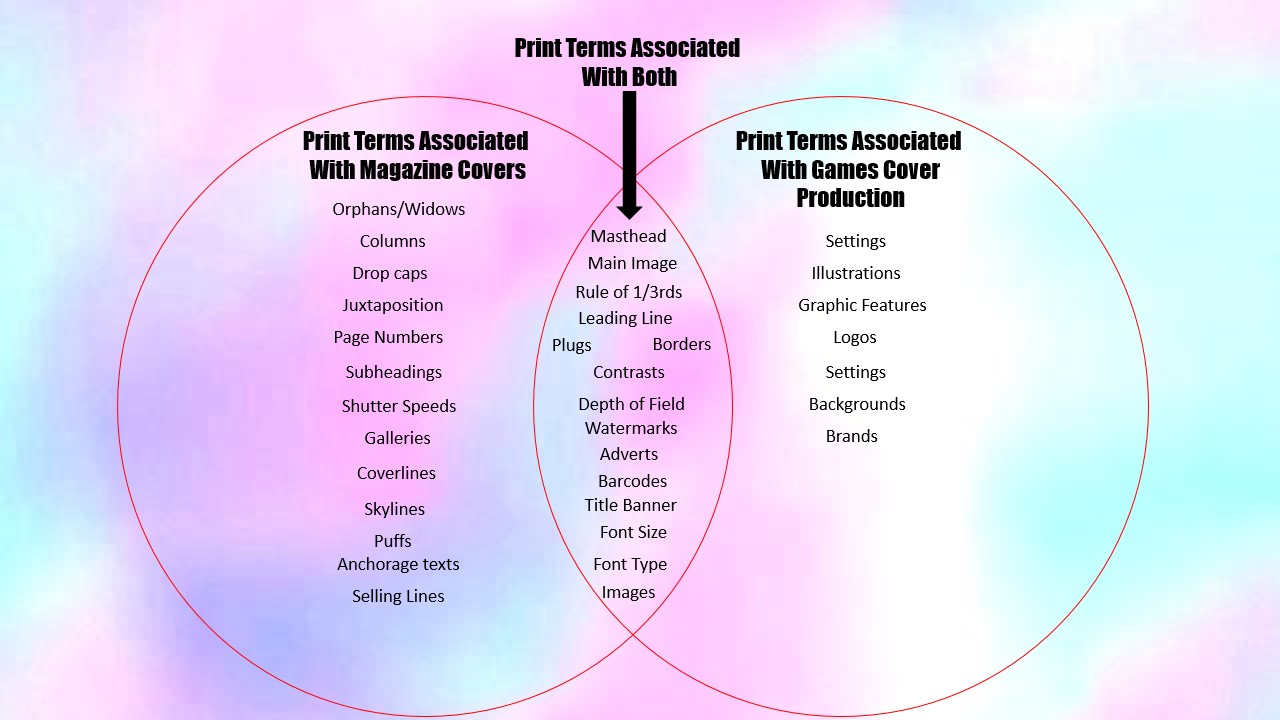
Venn Diagram – Comparing Games covers to Magazine covers


Print terms associated with magazine production
print terms associated with both
print terms associated with games cover production



Positive and negative stereotypes – positive stereotypes represent a “positive” evaluation of a group that typically signals an advantage over another group
Counter-types – a positive stereotype and emphasizes the positive features about a person. Used to break and go against the current stereotype.
Misrepresentation – the action or offence of giving a false or misleading account of the nature of something.
Selective representation – when some groups of people are represented more in government than others.
Dominant ideology – attitudes, beliefs, values, and morals shared by the majority of the people in a given society
Constructed reality –the theory that the way we present ourselves to other people is shaped partly by our interactions with others, as well as by our life experiences.
Hegemony – a way to describe people or ideas that become—and seek to remain—dominant in society
Audience positioning – he techniques used by the creator of a text to try to get the audience to understand the ideology of the text
David Gauntlett:
Fluidity of identity – the idea that identity is not fixed and can change depending on life and surroundings
Constructed identity – the shaping of a persons values influenced by cultural systems and individual actions
Negotiated identity – changing someone’s beliefs and identity by the use of cultural beliefs and the mass media
Collective identity – the shared sense of belonging to a group


Positive and negative stereotypes = a positive stereotype refers to a subjectively favourable belief held about a social group. However, negative stereotypes could be considered as the cognitive component of prejudice, which is defined as a general negative evaluation of a social group. Negative stereotypes are also related to discrimination, that is, to negative behaviours directed toward individuals because of their group membership.
Counter-types = they are positive stereotypes which emphasises the positive features about a person.
Misrepresentation = when you give a false and inaccurate representation of something, creating a misleading account of the nature of someone. For example, Pitbulls are represented as being very vicious, when in reality they are quite loving house dogs if you give them the correct training.
Selective representation = this is when some groups of people are represented more in the government than other groups of people.
Constructed reality = The term social construction of reality refers to the theory that the way we present ourselves to other people is shaped partly by our interactions with others, as well as by our life experiences.
Dominant ideology = the ideology of the dominant class. It denotes the attitudes, beliefs, values and morals shared by the majority of people in a given society.
Hegemony = it is a way to describe people or ideas that become and seek to remain dominant in the dominant ideology.
Audience Positioning = it is a technique used by the author of the text, which gets the audience to understand the ideology of a text.
David Gauntlet – Identity Terms
Fluidity of identity = Fluidity of Identity has the ability to change in many directions. For example, if a man on weekdays wore suits and masculine clothes (the apparel stereotype of males) , however on weekends, they decided to wear make-up, dresses and heels (the apparel stereotype of females).
Constructed Identity = this is when you shape a person’s beliefs, values or morals by individual actions.
Negotiated Identity = this is when people contemplate “who is who” with their identity. When the identity has been determined, people have to be respectful and agree to the identities people have taken. This means not making assumptions of gender.
Collective Identity = it is the shared identity of the group and its members.