- Barthes – French social and literary critic Roland Barthes is the leading structuralist thinker of the 20th Century. He draws on Saussure’s conception of semiotics: the science of the way signs behave within society. In particular, Barthes examines the arbitrariness of signs within communication systems, such as texts.
- Pierce – C.S.Peirce was a scientist and philosopher best known as the earliest proponent of pragmatism. An influential thinker and polymath, Pierce is among the greatest of American minds. His thought was a seminal influence upon William James, his life long friend, and upon John Dewey, his one time student.
- Saussure – Saussure argues that the goal of linguistics should be to identify the elements of a language, to classify them and finally describe the their combination rules in a syn-chronic structure. This view was in contrast with the predominant dia-chronic perspectives of that time.
- Semiotics – The study of signs and symbols and their use or interpretation.
- Sign – An object, quality, or event whose presence or occurrence indicates the probable presence or occurrence of something else.
- Signifier – A sign’s physical form (such as a sound, printed word, or image) as distinct from its meaning.
- Iconic sign – signs where the signifier resembles the signified, e.g., a picture.
- Signified – the meaning or idea expressed by a sign, as distinct from the physical form in which it is expressed.
- Indexical sign – signs where the signifier is caused by the signified, e.g., smoke signifies fire
- Symbolic sign – signs where the relation between signifier and signified is purely conventional and culturally specific, e.g., most words.
- Code – a system of words, letters, figures, or symbols used to represent others, especially for the purposes of secrecy.
- Ideology – a system of ideas and ideals, especially one which forms the basis of economic or political theory and policy.
- Paradigm – a typical example or pattern of something; a pattern or model.
- Syntagm – a widely held but false belief or idea. Make people believe a different idea.
- Signification – the representation or conveying of meaning.
- Denotation – What is actually there. What the image is.
- Connotation – What something represents.
- Myth – Myth in media analysis refers to how words and images are systematically used to communicate cultural and political meanings
- Anchorage – Some signs provide anchorage
- Dominant signifier
- A radical text – Challenges dominant ideology
- A reactionary text – supports dominant ideology
Daily Archives: 09/18/2019
Filters
Media Definitions
Definitions
- Barthes is one of the leading theorists of semiotics, the study of sign, connatation, denotation, myth.
- C S Pierce his categories of sign( iconic, indexical, symbolic)
- Saussure was a linguistic
- Semiotics is the study of sign process
- Sign is a motion or gesture
- Signifier a sign’s physical form for an example a printed word
- Signified the concept that the signifier refers to
- Iconic sign is when something is directly linked to something
- Indexical sign is when something is indirectly linked to an object
- Symbolic sign is a mark, sign or word that indicates a meaning
- Code has an agreed meaning to their audience
- Dominant Signifier is the main meaning of a word, the main sign
- Anchorage is the meaning of an image
- Ideology is a set of beliefs
- Paradigm is a collection of signs
- Syntagm is a relationship where signs occur in sequence or parallel and operate together to create a meaning
- Signification the process of making meaning
- Denotation the object
- Connotation is the meaning
- Myth in media analysis is how words and images are used to communicate political meanings
- A radical text is one that challenges the dominant ideology
- A reactionary text is a text supporting the ideology
Definitions/ Key Terms
- Barthes – the theorist who studied semiotics and developed the theory of semiotics
- Pierce – CS Pierce, a philosopher, theory of signs , indexical, iconic and symbolic
- Saussure – a swiss linguist and semiotician, the signifier and the signified
- Semiotics – the study of signs
- Sign – an object/thing/element
- Signifier – A signs physical form (sound, word, image or action)
- Signified – the meaning or idea expressed by a sign
- Iconic sign – a sign that has a direct connection to its object
- Indexical sign – a sign that has an indirect link to its object
- Symbolic sign – a sign that has a random link to its object
- Code – something that represents something and has meaning
- Dominant Signifier – a mainly accepted form of a sign.
- Anchorage – a dominant sin to fix meaning
- Dominant Ideology – a set of beliefs
- Paradigm – a collection of signs
- Syntagm – a sequence of signs
- Signifcation – the process of creating signs
- Denotation – what symbol/object is clearly/ obviously there, what you can see
- Connotation – what a symbol/object implies/ what its meaning is
- Myth – something thats made up but loads of people believe, Barthes suggests we should question them
- A radical text – challenges a dominant ideology
- A reactionary text. – supports dominant ideology
Definitions
Barthes, A leading theorist of the study of semiotics.
Pierce, Theorist that investigated iconic, indexical and symbolic signs.
Saussure, A Swiss semanticist and linguist. (signified and signifier)
Semiotics, the study of signs and symbols.
Sign, A signal or an action that gives instruction and information.
Signifier, a physical sign (sound, image or printed)
Signified, The meaning or idea that has been expressed by a sign.
An Iconic sign,
which has a direct connection to its’ object (ie it looks or sounds like the object)
An Indexical sign,
which has an indirect link to its’ object (think smells)
An Symbolic sign,
which has a random or arbitary link based on a shared knowledge or an agreement, for example, a shared culture or language (think letters, words, writing, shapes, squiggles, colours, sound effects, facial expressions, hand gestures, clothing, hair styles, etc)
Code, A series of numbers, words or symbols that represents something and has meaning.
Dominant Signifier, The main meaning of a sign.
Anchorage, Anchor fixes your meaning the sign that provides clear meaning.
Ideology,
a system of ideas and ideals.
Paradigm,
a typical example or pattern of something.
Syntagm,
unit with a set of linguistic forms that are in a sequential relationship to one another. A sequence of signs.
Signifcation,
Representation or conveying of meaning. Process of creating signs.
Denotation,
the literal or primary meaning of a word.
Connotation,
The idea or feeling which a word invokes for a person.
Myth, A false belief, idea or story that isn’t 100% true.
Dominant Ideology, Dominant set of beliefs/ideas
A radical text, challenges a dominant ideology
A reactionary text, supports dominant ideology
Key Terms
Barthes- a french philosopher who developed the ideas of semiotics.
Pierce- an american philosopher who studied the idea of different ways of communication and the idea that things could be split into three sections, iconic, symbolic or indexical.
Saussure- was a Swiss linguist and semiotician. He theorised in language and the connections between their meanings associated with the language. He developed the ideas of signified and
Semiotics- the study of signs and symbols and how to interpret them.
Sign- an object or gesture that shows an intention or idea.
Signifier- a signs physical form for example sound. (Saussure)
Signified- the meaning of a something expressed by a sign. (Saussure)
An Iconic Sign- a representative symbol of an object or person for example a picture of the queen.
An Indexical sign- An indirect communication for example colour
A Symbolic Sign- letters
Code- a communication of rules or orders.
Dominant Signifier- main sign for example the JEP’s dominant sign is the tile JEP.
Anchorage- the fixing of meaning towards the sign
Ideology- a set of ideas or beliefs
Paradigm- a collection of signs
Syntagm- a sequence of signs that work together. Number of signs need each other for it to be right or make sense.
Signifcation- the representation or conveying of meaning.
Denotation- the object
Connotation- the meaning of the word
Myth- a belief that lots of people believe in however it isn’t true.
Radical text- challenges a dominant ideology.
A Reactionary Text- supports dominant ideology.
Dominant Ideology- dominant attitudes ideas and beliefs.

AS Summer Task

- An iconic sign – which has a direct connection to its’ object (ie it looks or sounds like the object)
- An indexical sign – which has an indirect link to its’ object (think smells)
- A symbolic sign – which has a random or arbitary link based on a shared knowledge or an agreement, for example, a shared culture or language (think letters, words, writing, shapes, squiggles, colours, sound effects, facial expressions, hand gestures, clothing, hair styles, etc)
Iconic sign- picture of game character is a direct link to the actual character
Indexical sign- character holding a weapon is an indexical sign to violence
Symbolic sign- play-station logo, background colour
C S Pierce
3 Different types of signs
Symbolic- has a random link to its object e.g. color, shapes, textures.
Indexical- a sign that has a link to its object e.g. sounds, props.
Iconic- a sign that looks like an object e.g. sets, camera work.
Signs on my Pre As poster.
Symbolic- the letters and text in my poster are symbolic as they can be interpreted any way you like.
Indexical- the colour of the fonts, for example blue makes me thinks of calm and red makes me think of anger. The picture of pac man could be indexical to childhood and youth as well as old fashion.
Iconic- pac man, and the picture of the character firebreak
C S Pierce

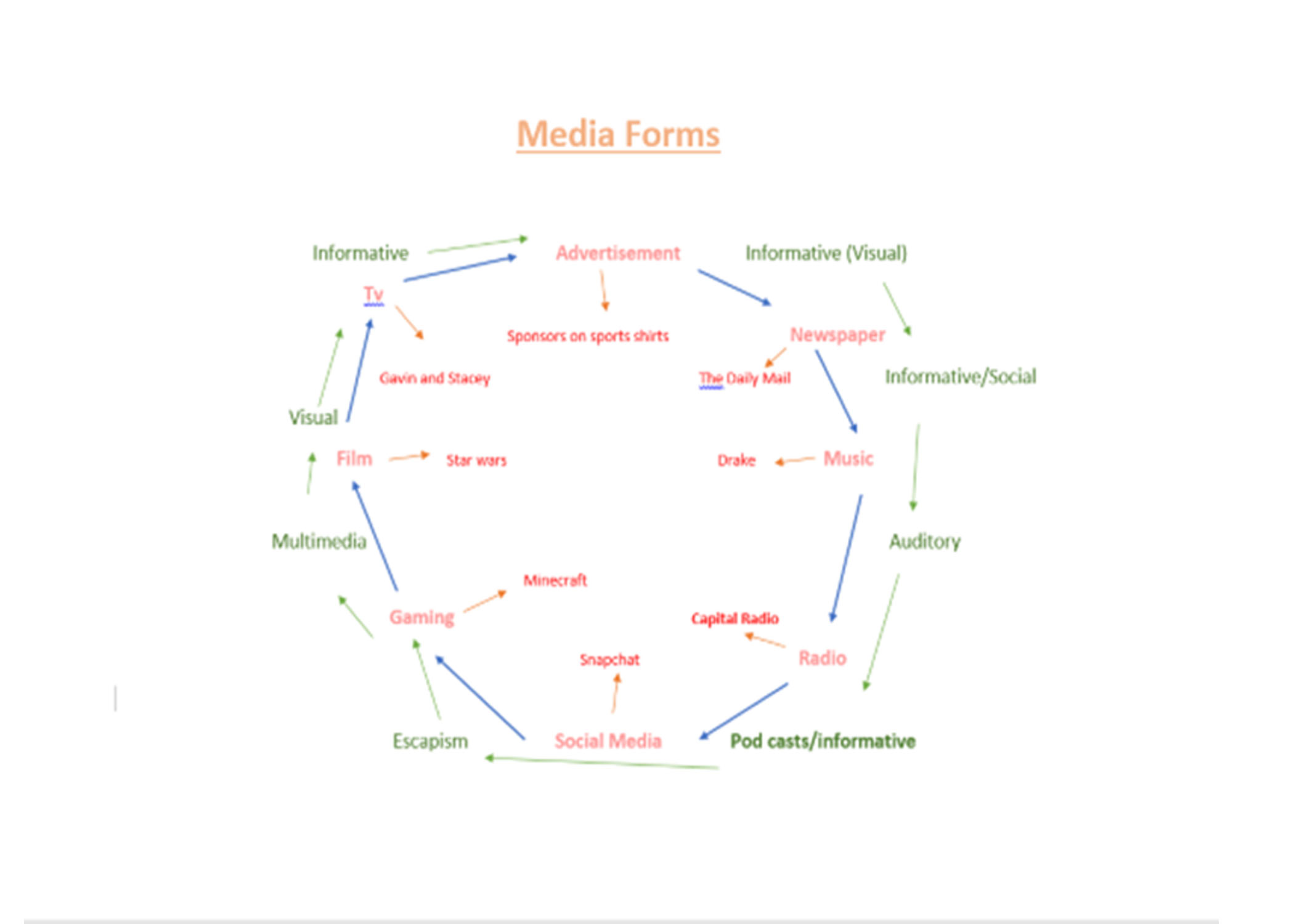
Media Forms