 | ||
 | ||
 |
All posts by Phoebe Baudains
Filters
DEFINITION OF EDITING
The definition of editing, in film is “to prepare (motion-picture film, video, or magnetic tape) by deleting, arranging, and splicing, by synchronizing the sound record with the film, etc.” A sequence is a number of scenes joined together that could be a large percentage of the movie when it is finished.

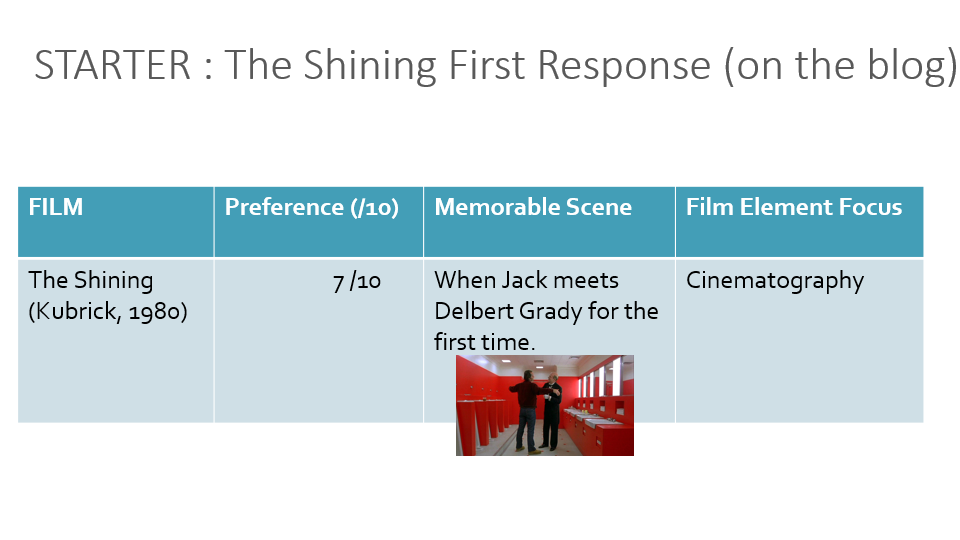
THE SHINING FIRST RESPONSE
ACTIVITY 2 (SHOT DISTANCES)
Give an example of where at least 3 of these shots were used in a film that you have watched and the effect on you as the viewer.
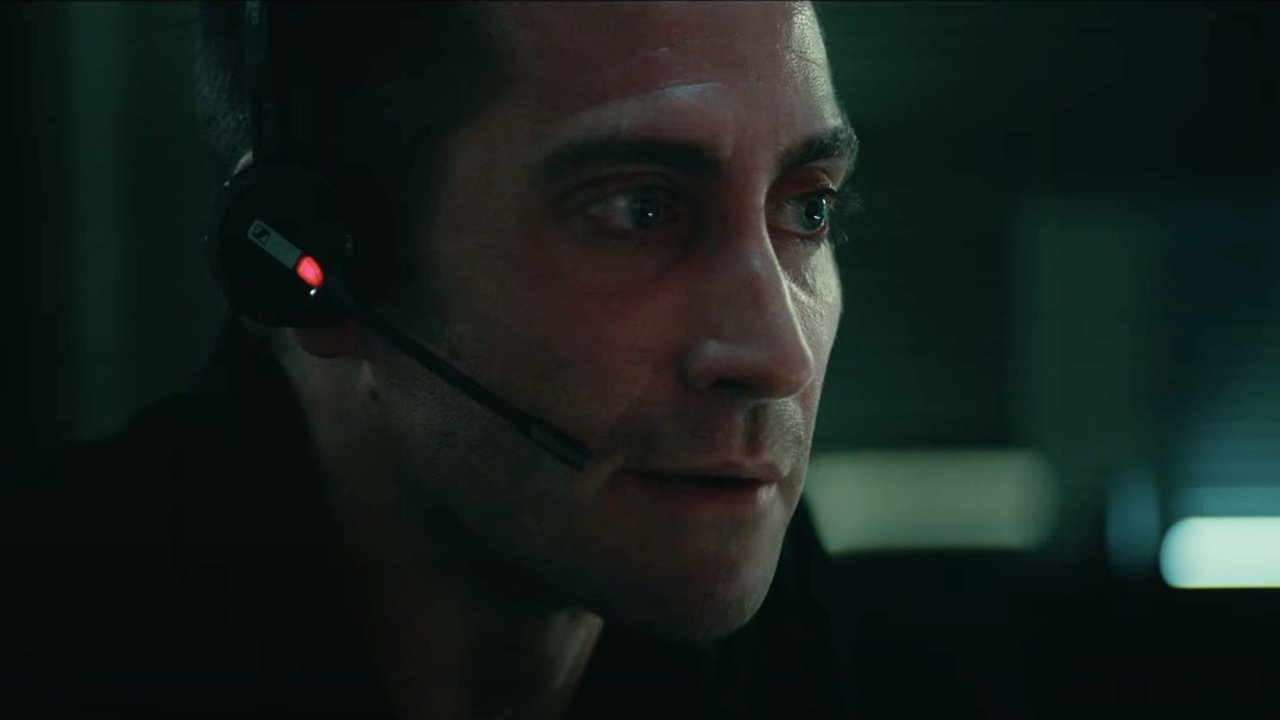
The close up: The use of the close up in this movie (The Guilty) is used as a realization shot, where the character realizes an important factor of the movie. This shot created tension and fear and it really shows the characters thoughts and emotions by getting up close to his face.

The extreme long shot: The extreme long shot in this film (Harry Potter and the Philosopher’s stone) is used as an establishing shot, creating the world and scenery of the world. By doing this it created a sense of realism as it introduced us directly, showing us by using an extreme long shot.

The extreme close-up: An extreme close-up shot frames a subject very closely, often so much so that the outer portions of the subject are cut off by the edges of the frame. On an actor, this is commonly used to show specific portions of the body, like the face or hip, but it can go closer to show only an actor’s mouth, or even a single eye. In this shot the extreme close up is used to express the characters emotions without using dialogue.

FIRST GROUP SHOT REFLECTION
I wasn’t here.
Blog checklist
- Summer Task (What makes a good film? )
- Activity 1 Induction slides :Connecting the IB Learner Profile to Film Studies
- Activity 2 Induction slides: Categorising Film.
- Activity 3 Induction Slides : Identify a Formula for Box Office Hits
- Mise en Scene “Chaotic vs Anally Tidy” Examples.
- Mise en scene definition
- Mise en Scene Choose a Film which you think demonstrates “excellent use of Mise en Scene” and explain why. (Remember to illustrate your ideas with still images from the film!)
- Homework WK 1: (20 /09/21) Film as Art “Spectrum” Activity (from Monaco How to Read a Film).
- Bladerunner First Response and Memorable Scene
- Homework WK 3: (27 /09/21) Bladerunner Mise En Scene Essay (E MAIL TO ME DIRECT)
- Cinematography/Cinematographer definition (28/9/21)
- Diegetic, Intradiegetic, Extradiegetic gaze examples (30/9/21)
- Shot Distances Examples (1/10/21)
- Shot Angles Examples (1/10/21)
- Shot Movement Examples (1/10/21)
- Shot Types Table (4/10/21)
DEPTH OF FIELD
Shallow focus: Shallow focus is a cinematographic technique incorporating a small depth of field. In shallow focus, one plane of the scene is in focus while the rest is out of focus. Shallow focus is typically used to emphasize one part of the image over another. For example in the movie Red Lights, this character (Tom Buckley) is in focus and the main attention, while the background is blurred indicating the audiences focus onto him.
![Red Lights | The Personality Database [PDB] | Movies](https://www.personality-database.com/profile_images/201763.png)
Deep focus: Deep focus is a cinematographic technique using a large depth of field. Depth of field is the front-to-back range of focus in an image, or how much of it appears sharp and clear. In deep focus, the foreground, middle ground, and background are all in focus.

| Name Of Shot | Description of shot in relation to subject | Use In Storytelling |
| Extreme Close-up (XCU) | Part of the face takes up the entire screen. (eyes, mouth e.g.) | Gets inside the head and thoughts of the character. |
| Close-up (CU) | Whole characters face takes up screen. | Reveals characters emotional state. |
| Medium Close-up (MCU) | Characters head and shoulders in frame. | Subjects emotions and a little of their surroundings. |
| Low Angle (LA) High angle (HA) | Waist/knees upwards. | Shows if and which characters are in power and whose who are not. Intimidated or intimidator. |
| Extreme Long Shot (XLS) | Only scenery visible, Characters barely or not visible. | Used as an establishing shot. |
| Medium Shot (MS) | One or two characters in frame from waist height or sometimes over the shoulder of one of the characters (OOS) | Often used as a master shot/Two shot/shot-reverse for conversations |
| Pan/ Tilt | Camera moves across the horizon/camera moving up and down. | Mimics a static character looking around. |
| Track (on a Dolly, steadicam or handheld) | Camera follows subject moving along with the character. | Audience is following the action, more involved. |
ACTIVITY 3 (SHOT ANGLES)
Give an examples of where at least 3 of these shots were used in a film that you watched and explain the effect on you as a viewer.
Eye Level shot–
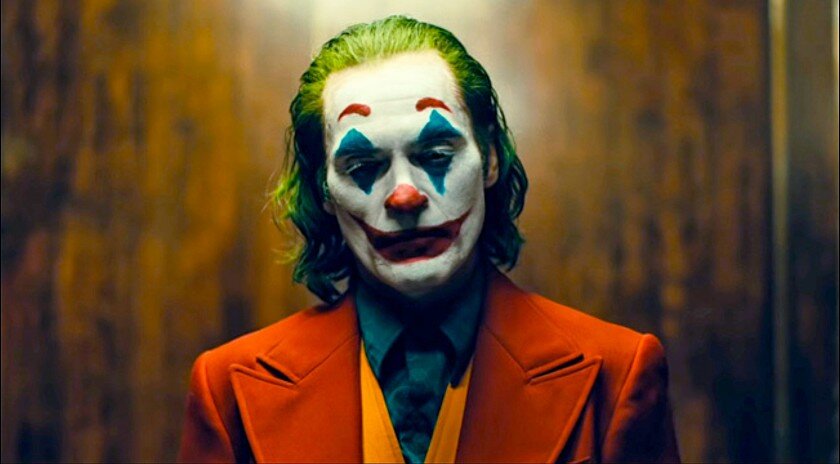

The shoulder level shot-

Low angle shot-

THE IB LEARNER PROFILE AND FILM STUDIES
Communicators – They are able to communicate and understand different ideas.
Reflective – They look over their work, reflecting in order to improve if possible.
Risk takers – They step out their comfort zone and create something new to them.
Open-minded – They take in all different perspectives and they’re open to different ideas.
Knowledgeable – They understand the subject of what they are filming and how to film it the way they want.
Principled – They always have good intentions.
Caring – Do not promote anything dangerous or offensive.
Thinkers – Usually come up with original and creative ideas.
Inquirers – They make the audience question topics.
Balanced – They have a balanced mind. They don’t focus on just one topic at a time, always thinking about the whole production.
