one point perspective

symmetry

deep focus

steadicam tracking shots

one point perspective

symmetry

deep focus

steadicam tracking shots

One Point Perspective: when all horizontal lines, if you were to extend them they would come to a point usually in the centre of the frame. (Source: https://www.nyfa.edu/student-resources/stanley-kubrick-one-point-perspactive/#:~:text=A%20one%2Dpoint%20perspective%20shot,track%20disappearing%20in%20the%20distance.)

Symmetry: the quality of being made up of exactly similar parts facing each other or around an axis (Source: https://www.google.com/search?q=symmetry+definition+&safe=active&bih=937&biw=1920&rlz=1C1GCEA_enJE970JE970&hl=en&sxsrf=AOaemvLIXSgqhoYKxRnN8GfcBSN3bkD0ZA%3A1633510454267&ei=NmRdYYrUD9SD8gL3loC4DQ&ved=0ahUKEwiKx_PStLXzAhXUg)

Deep Focus: In filmmaking, deep focus refers to a technique where all elements of an image—foreground, middle ground, and background—are all in sharp focus. (Source:https://www.masterclass.com/articles/how-to-use-a-deep-focus-shot-when-making-a-film#:~:text=In%20filmmaking%2C%20deep%20focus%20refers,imbue%20their%20shots%20with%20detail.)

Steadicam: A Steadicam is a camera stabilizing system used to capture tracking shots with motion picture cameras. It isolates the camera operator’s movement and makes the shot look smooth and controlled, capturing the action without any wobbles. (Source: https://www.masterclass.com/articles/what-exactly-is-a-steadicam-understanding-the-groundbreaking-camera-stabilizer-that-changed-hollywood)

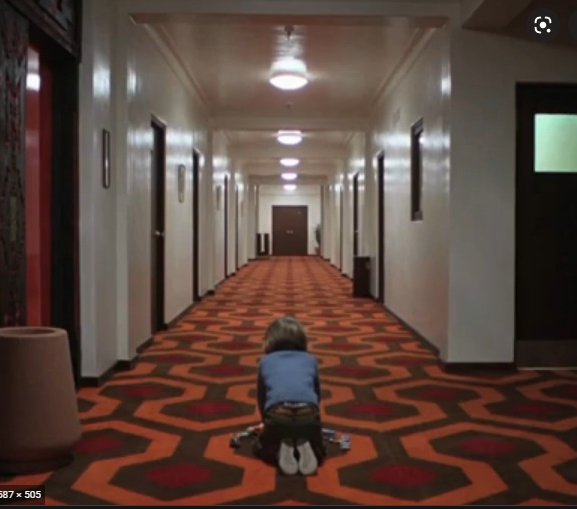
One point perspective is the horizon of the shot and how it directs the viewers attention using the horizon and framing. An example of this would be a famous shot from The Shining(1980, Kubrick) He used One point perspective in a scene where a tracking steadicam shot follows Danny through the house and he eventually runs into the Grady twins at the end of a corridor, this narrow corridor creates a very vivid framing for the scene which acts as a guide for the viewers attention, this guide directs the observers attention towards the Grady twins and because of the One Point perspective the viewer is almost forced to keep looking at the twins almost as if there is no where else for them to look. This scene can be seen to imply a sense of no escape, as if the family is trapped in this house for the winter and the ‘Exit’ sign on the right side of the shot creates a sense of irony while also hinting to the idea of the family being trapped.

Symmetry is a technique which makes a shot seem unnatural, it reduces the verisimilitude within the narrative. But a shot which uses symmetry can be visually stunning and done right can attract the viewers attention more and get the observer more interested in the film. A symmetrical shot can be used to imply an idea, such as a mundane routine, A director/cinematographer could use symmetry to emphasise the idea and concept of a mundane routine which a character may follow. Furthermore, another example of where a film COULD use symmetry is if a character is lost, whether that be a maze or not, a good example of this is scene in The Shining(1980, Kubrick)

Deep focus is where everything in the shot is in focus, the background, foreground e.tc. In Citizen Kane(1941, Orson Welles) deep focus is used to display to the viewer all the context and information about the argument/discussion that they’re having. To further explain- the parents are the closest and therefore the biggest in the shot, this is because they have the most power in this situation since they’re arguing about their son. The other person, who’s trying to persuade the parents to sign over their son is further from the camera than the parents because he has less control/power in the situation. In the far background, through the window in shot, the boy is playing outside in the snow – this would make him the furthest from the camera and this has obviously been done to convey the message that the boy is oblivious to what’s happening inside.

Steadicam tracking is when a cameraman uses a steadicam while tracking the character or object. This is commonly used when the camera is following a characters who’s running away from something, and this can be seen to convey the message that the thing that’s chasing them(if anything chasing them) is getting closer, this technique builds huge suspense, tension and anxiety for the viewers especially in horror films where that’s the goal. In The Shining(1980, Kubrick) this was used brilliantly is one of the ending scenes where Danny is running away from Jack in a maze, The tracking shot is accompanied with a eye-level shot from behind Danny, which creates more tension on top of the tracking shot because is could emphasise to the viewer that Danny is only a small kid, which would create more sympathy/empathy within the viewer for Danny.

One Point Perspective – All focus goes to one vanishing point on the horizon. The easiest example to visualise would be a corridor.
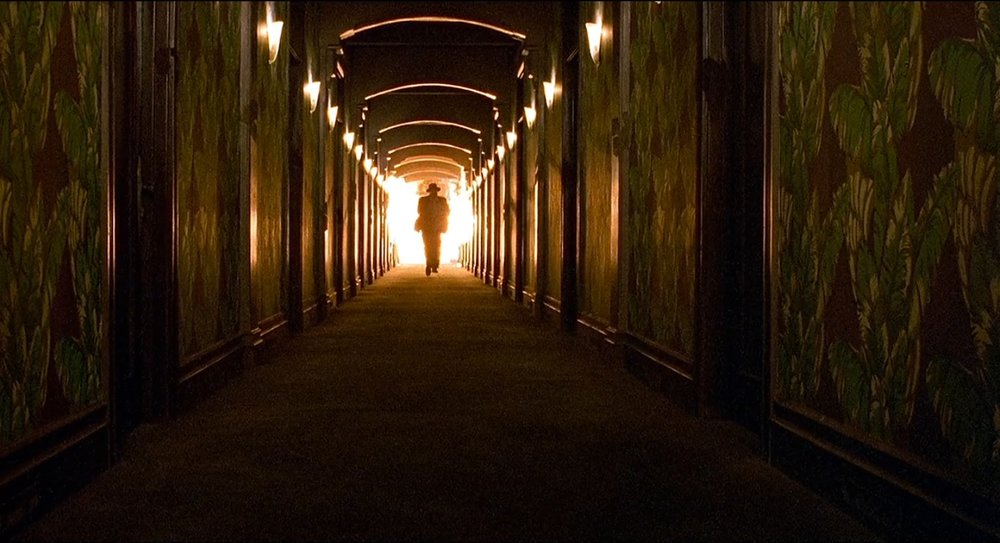

Symmetry – The set reflects itself along the centre axis which the camera is aligned on as if through a mirror.
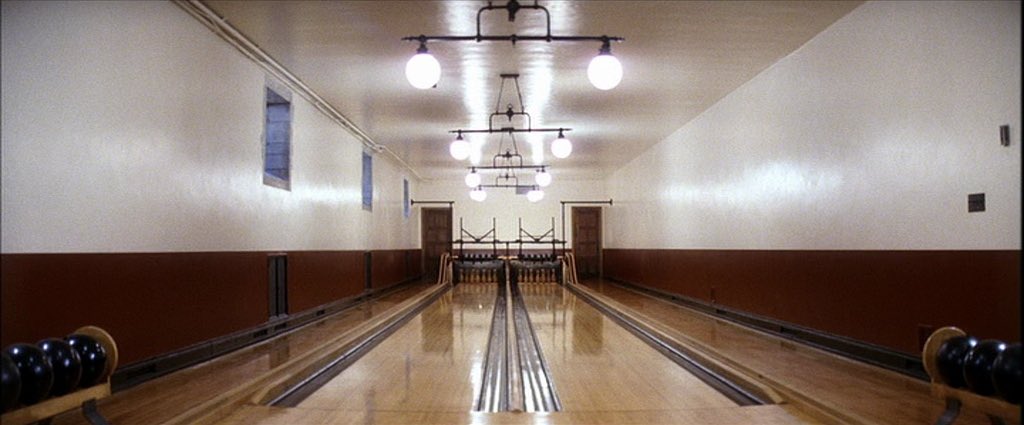

Deep Focus – The focus is on the foreground, midground and background.

Steadicam Tracking Shots – The camera tracks a character or object through a scene but the camera is suspended between axes such that the movement of the camera is independent of the stabilizer or cinematographer

One point perspective:
The art of crafting shots in film with complete or near symmetry. The technique is used to build tension or represent a characters mental/emotional state state. The composition of these shots draws the viewer to a specific focal point within the frame (i.e, the centre).

Symmetry:
Symmetry is the organised composition in where the material/environment/subject is mirrored within the frame. The shot is meant to make the audience feel as if they are being dragged into the shot itself.
Deep focus:
Deep focus refers to a technique where all elements of an image- foreground, middleground, and background- are all in sharp focus.
Steadicam tracking shots:
Shots where the camera follows a subject forward or alongside the subject. The camera is mounted onto a dolly and placed onto rails.
One Point Perspective- the craft of shots with some form of symmetry. Also the main focus is placed in the middle.

Symmetry- Balanced proportions. Usually used to refer to an object that is invariant under some transformations; including translation, reflection, rotation or scaling. (WIKIPEDIA)

Deep Focus- Deep focus is a style or technique of cinematography and staging with great depth of field. A deep-focus shot includes foreground, middle-ground, and extreme-background objects, all in focus. (COLUMBIA FILM LANGUAGE GLOSSERY)

Steady cam tracking shots- When the camera is either handheld or on a track and follows the character or moves around the scene backwards/forwards/side to side.

One Point Perspective- One-point perspective is a way of crafting cinematic shots with near-perfect symmetry. The composition of these shots draws the viewer’s eye to a specific focal point within the frame, absorbing them into the dimension of the shot and manipulating the experience by telling them exactly where to look

Symmetry- Symmetry refers to material being organized in such a way that it conveys a sense of unity through the repetition of one or more elements.

Deep Focus -In filmmaking, deep focus refers to a technique where all elements of an image—foreground, middleground, and background—are all in sharp focus.

Steadicam Tracking Shots- In cinematography, a tracking shot is any shot in which the camera physically moves sideways, forward, or backward through the scene. Tracking shots usually last longer than other shots, follow one or more moving subjects, and immerse the audience in a particular setting
