Daily Archives: October 16, 2019
Filters
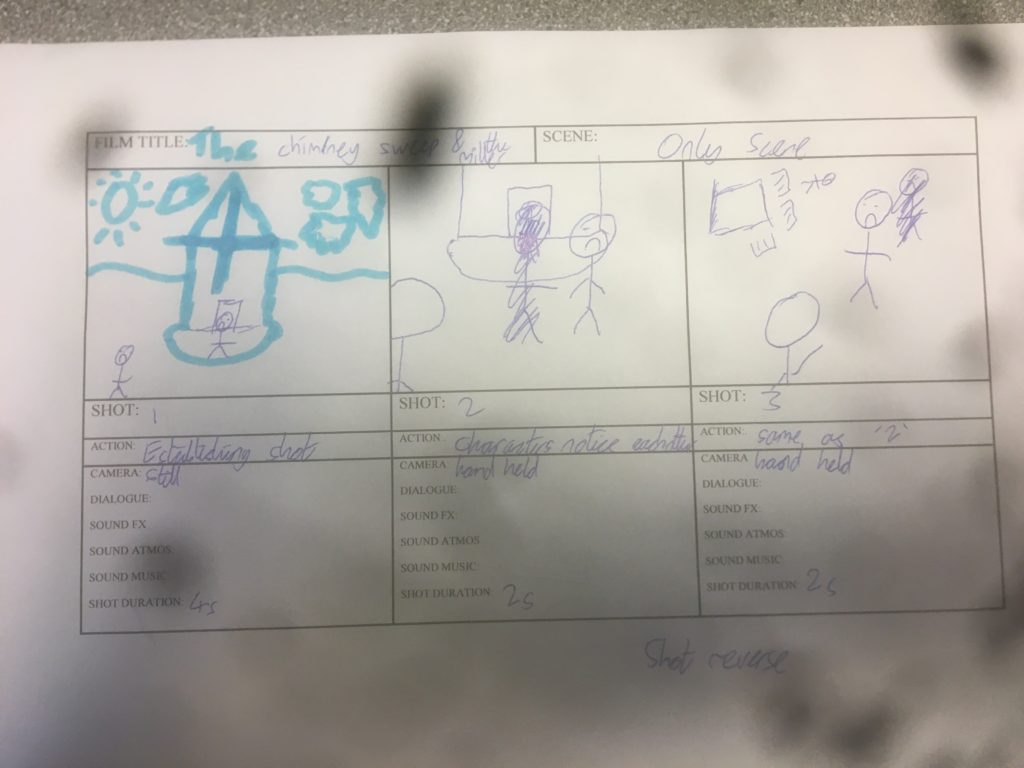
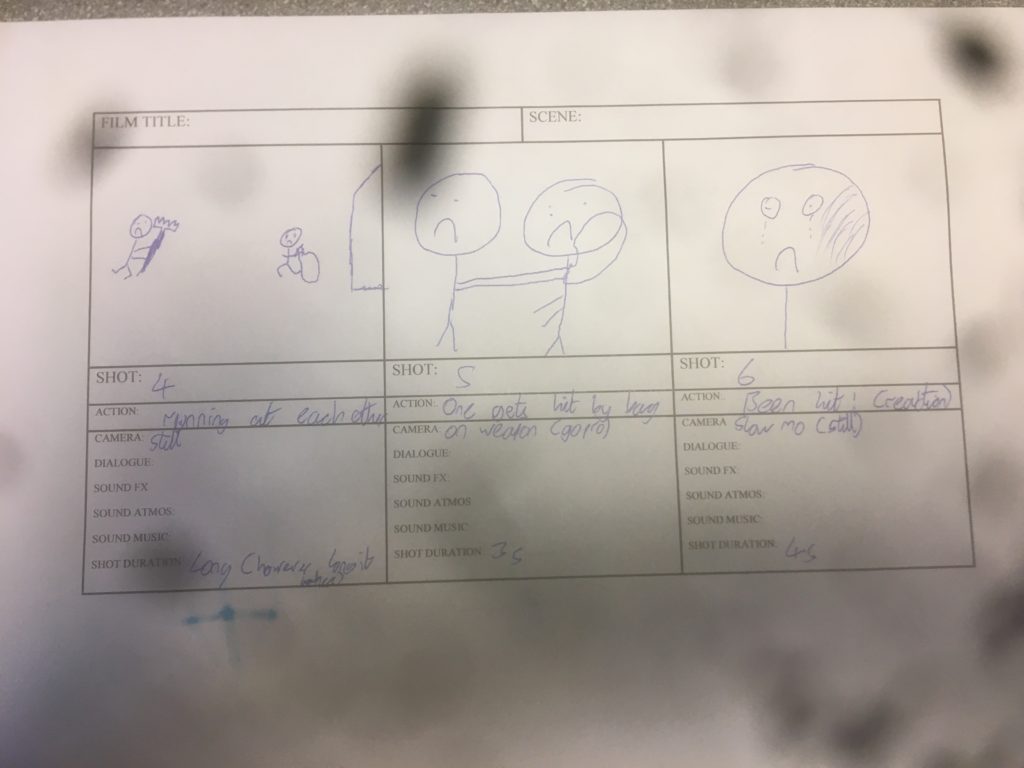
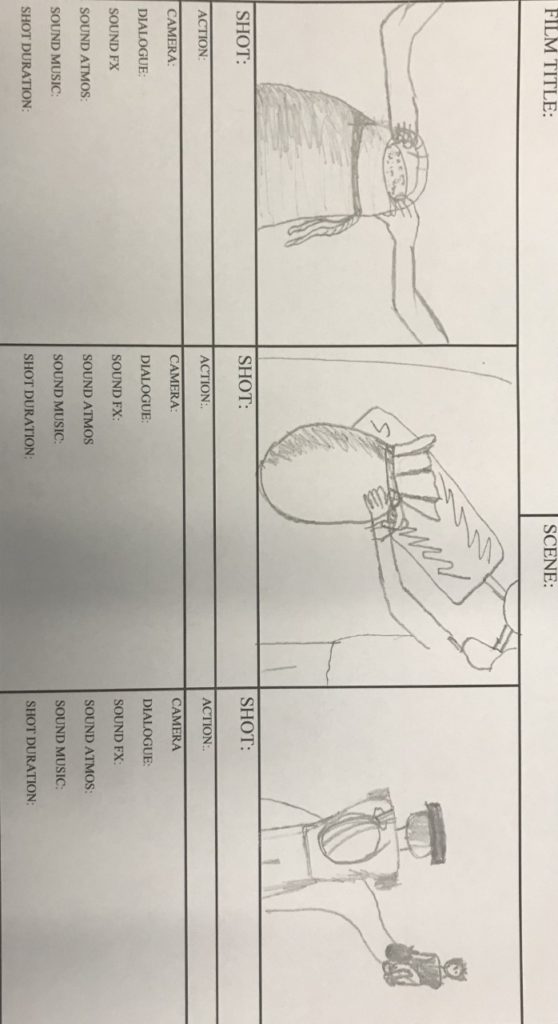
Chimney Sweep and Miller scene – own story board
Editing Techniques – Micro Elements of Film
TASK: Find examples from films, explaining why the director has chosen to use this cut. Write into the spaces underneath each definition and paste URL’s for the clips you use to illustrate/evidence your argument.
Cut: The most common editing technique. Two pieces of film are spliced together so that the film “cuts” from one image to another. (Jump Cut/ Match Cut) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wv3Hmf2Dxlo
Fade: Can be to or from black or white. A fade can begin in darkness and gradually assume full brightness (fade-in) or the image may gradually get darker (fade-out). A fade often implies that time has passed or may signify the end of a scene.
Dissolve: A kind of fade in which one image is slowly replaced by another. It can create a connection between images.
Wipe: A new image wipes off the previous image. A wipe is more fluid than a cut and quicker than a dissolve.
Flashback: Cut or dissolve to action that happened in the past.
Shot-Reverse-Shot: A shot of one subject, then another, then back to the first. It is often used for conversation or reaction shots.
Cross Cutting: Cuts between actions that are happening simultaneously. This technique is also called parallel editing. It can create tension or suspense and can form a connection between scenes.
Eye-Line Match: Cut to an object, then to a person. This technique shows what a person seems to be looking at and can reveal a character’s thoughts.